B+ 树:搜索、插入和删除操作示例
什么是 B+ 树?
B+ 树主要用于实现多级动态索引。与 B 树相比,B+ 树仅在树的叶子节点存储数据指针,这使得搜索过程更加准确和快速。
B+ 树的规则
以下是 B+ 树的基本规则。
- 叶子节点用于存储数据记录。
- 它存储在树的内部节点中。
- 如果目标键值小于内部节点,则会遵循其左侧的指针。
- 如果目标键值大于或等于内部节点,则会遵循其右侧的指针。
- 根节点至少有两个子节点。
为什么使用 B+ 树
以下是使用 B+ 树的原因:
- 键主要用于通过指向正确的叶子节点来辅助搜索。
- B+ 树使用“填充因子”来管理树的增加和减少。
- 在 B+ 树中,由于内部节点不关联数据,因此可以在内存页上轻松放置多个键。因此,可以快速访问叶子节点上的树数据。
- 由于 B+ 树的所有叶子节点都相互链接,因此对所有元素的完整扫描只需要一次线性遍历。
B+ 树 与 B 树
以下是 B+ 树与 B 树的主要区别:
| B+ 树 | B 树 |
|---|---|
| 搜索键可以重复。 | 搜索键不能重复。 |
| 数据仅存储在叶子节点上。 | 叶子节点和内部节点都可以存储数据。 |
| 存储在叶子节点上的数据使搜索更准确、更快速。 | 由于数据存储在叶子节点和内部节点上,搜索速度较慢。 |
| 删除不难,因为元素只从叶子节点中移除。 | 删除元素是一个复杂且耗时的过程。 |
| 链接的叶子节点使搜索高效快捷。 | 您不能链接叶子节点。 |
搜索操作
在 B+ 树中,搜索是最容易执行的操作之一,并且可以从中获得快速准确的结果。
适用的搜索算法如下:
- 要查找所需记录,您需要对树中的可用记录执行 二分查找。
- 如果搜索键完全匹配,则会将相应的记录返回给用户。
- 如果父节点、当前节点或叶子节点中的搜索未找到确切键,则会向用户显示“未找到”消息。
- 可以重新运行搜索过程以获得更好、更准确的结果。
搜索操作算法
1. Call the binary search method on the records in the B+ Tree.
2. If the search parameters match the exact key
The accurate result is returned and displayed to the user
Else, if the node being searched is the current and the exact key is not found by the algorithm
Display the statement "Recordset cannot be found."
输出:
显示与确切键匹配的记录集;否则,向用户显示失败尝试。
插入操作
以下算法适用于插入操作:
- 节点中 50% 的元素被移动到新的叶子节点进行存储。
- 新叶子的父节点与最小键值以及树中的新位置正确链接。
- 如果父节点已满,则将其拆分为更多位置。
- 现在,为了获得更好的结果,中心键与该叶子的顶层节点相关联。
- 在找到顶层节点之前,请继续迭代上述步骤中解释的过程。
插入操作算法
1. Even inserting at-least 1 entry into the leaf container does not make it full then add the record
2. Else, divide the node into more locations to fit more records.
a. Assign a new leaf and transfer 50 percent of the node elements to a new placement in the tree
b. The minimum key of the binary tree leaf and its new key address are associated with the top-level node.
c. Divide the top-level node if it gets full of keys and addresses.
i. Similarly, insert a key in the center of the top-level node in the hierarchy of the Tree.
d. Continue to execute the above steps until a top-level node is found that does not need to be divided anymore.
3) Build a new top-level root node of 1 Key and 2 indicators.
输出:
该算法将确定元素并将其成功插入到所需的叶子节点中。
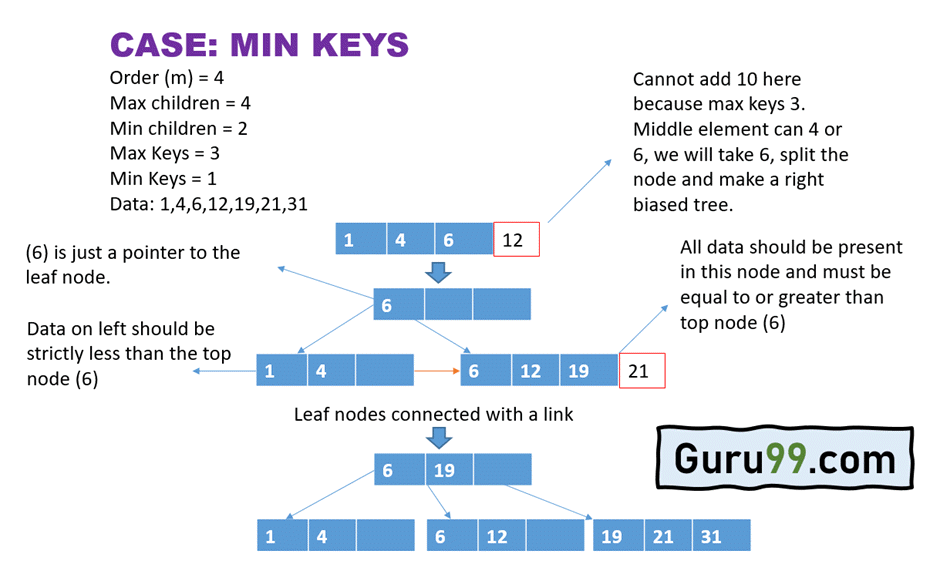
上面的 B+ 树示例将在下面的步骤中进行解释。
- 首先,我们有 3 个节点,前 3 个元素 1、4 和 6 被添加到节点中的相应位置。
- 系列数据中的下一个值是 12,它需要成为树的一部分。
- 为实现此目的,请拆分节点,并将 6 添加为指针元素。
- 现在,创建了一个树的右层级,并相应地调整了其余数据值,同时牢记大于或等于值的规则,这些值针对右侧的键值节点。
删除操作
B+ 树中删除过程的复杂性超过了插入和搜索功能。
删除 B+ 树中的元素时,适用以下算法:
- 首先,我们需要找到树中持有键和指针的叶子条目。如果叶子满足记录删除的确切条件,则从树中删除叶子条目。
- 如果叶子节点仅满足半满的因子,则操作完成;否则,叶子节点条目最少,无法删除。
- 右侧和左侧的其他链接节点可以腾出任何条目,然后将它们移动到叶子节点。如果未满足这些条件,则应将叶子节点及其链接节点合并到树层级结构中。
- 在叶子节点与其右侧或左侧邻居合并后,叶子节点或指向顶层节点的链接邻居中的值条目将被删除。
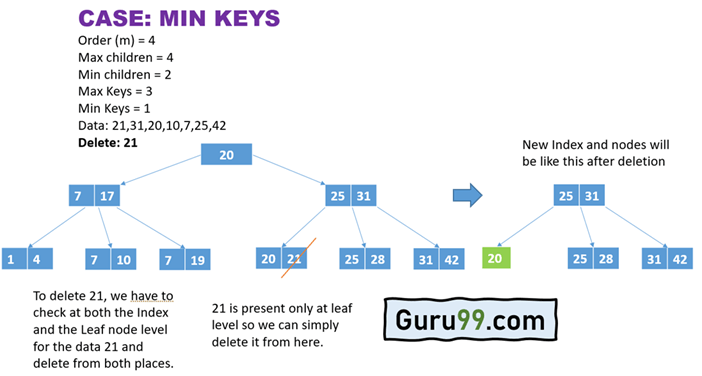
上面的示例说明了删除特定顺序的 B+ 树中元素的程序。
- 首先,在树中识别要删除的元素的精确位置。
- 在此,元素只能在叶子级别准确识别,而不能在索引放置处识别。因此,可以在不影响删除规则(即最小键值)的情况下删除该元素。
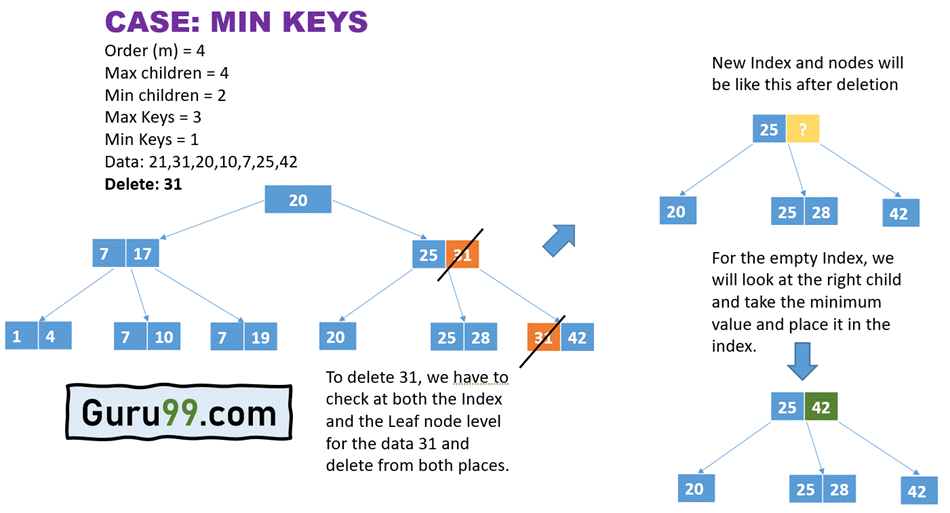
- 在上例中,我们需要从树中删除 31。
- 我们需要查找索引和叶子中 31 的实例。
- 我们可以看到 31 同时存在于索引节点和叶子节点级别。因此,我们从这两个实例中删除它。
- 但是,我们需要填充指向 42 的索引。现在我们将查看 25 下方的右子节点,取最小值并将其作为索引。因此,由于 42 是唯一存在的值,它将成为索引。
删除操作算法
1) Start at the root and go up to leaf node containing the key K
2) Find the node n on the path from the root to the leaf node containing K
A. If n is root, remove K
a. if root has more than one key, done
b. if root has only K
i) if any of its child nodes can lend a node
Borrow key from the child and adjust child links
ii) Otherwise merge the children nodes. It will be a new root
c. If n is an internal node, remove K
i) If n has at least ceil(m/2) keys, done!
ii) If n has less than ceil(m/2) keys,
If a sibling can lend a key,
Borrow key from the sibling and adjust keys in n and the parent node
Adjust child links
Else
Merge n with its sibling
Adjust child links
d. If n is a leaf node, remove K
i) If n has at least ceil(M/2) elements, done!
In case the smallest key is deleted, push up the next key
ii) If n has less than ceil(m/2) elements
If the sibling can lend a key
Borrow key from a sibling and adjust keys in n and its parent node
Else
Merge n and its sibling
Adjust keys in the parent node
输出:
删除键“K”,如有必要,从兄弟节点借键来调整 n 及其父节点中的值。
摘要
- B+ 树是一种自平衡的 数据结构,用于对数据执行准确、快速的搜索、插入和删除过程。
- 由于遍历链接的树结构使其高效,因此我们可以轻松检索完整数据或部分数据。
- B+ 树结构会随着存储记录数量的增加/减少而增长和收缩。
- 将数据存储在叶子节点以及后续的内部节点分支可以明显缩短树的高度,从而减少磁盘输入输出操作,最终消耗更少的存储设备空间。