数据结构中的基数排序算法
什么是基数排序算法?
基数排序是一种非比较排序算法。它通过对要排序的元素的各个数字进行分组来实现。然后使用一种稳定的排序技术来根据元素的基数对元素进行组织。它是一种线性排序算法。
排序过程涉及以下属性
- 找到最大元素并获取该元素的位数。这告诉我们排序过程将进行的迭代次数。
- 在每次迭代中,将元素相同有效位数的各个数字进行分组。
- 分组过程将从最低有效数字开始,到最高有效数字结束。
- 根据该有效位数的数字对元素进行排序。
- 保持具有相同键值的元素的相对顺序。基数排序的这一属性使其成为一种稳定的排序。
最后一次迭代将得到一个完全排序的列表。
基数排序算法的工作原理

让我们尝试使用基数排序算法按升序对上图中所示的整数列表进行排序。
以下是执行基数排序过程的步骤
第一步) 确定列表中值最大的元素。在这种情况下,它是 835。
第二步) 计算最大元素的位数。835 正好有 3 位数字。
第三步) 根据第二步确定迭代次数。835 有 3 位数字,这意味着迭代次数将为 3。
第四步) 确定元素的基数。由于这是十进制系统,基数将为 10。
第五步) 开始第一次迭代。
a) 第一次迭代
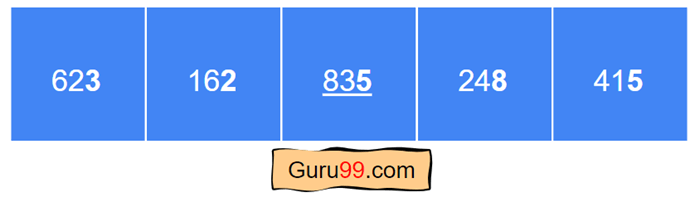
在第一次迭代中,我们考虑每个元素的个位值。
第一步) 将整数取模 10 以获得元素的个位数。例如,623 mod 10 得到 3,248 mod 10 得到 8。
第二步) 使用计数排序或其他稳定排序,根据元素的最低有效数字对整数进行组织。如上图所示,248 将落入第 8 个桶。623 将落入第 3 个桶,依此类推。
第一次迭代后,列表现在看起来像这样。
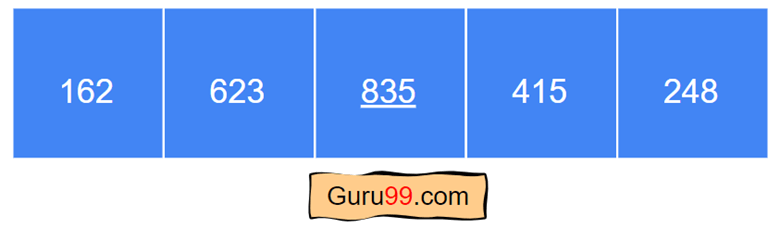
从上图可以看出,列表尚未完全排序,需要更多迭代才能完全排序。
b) 第二次迭代
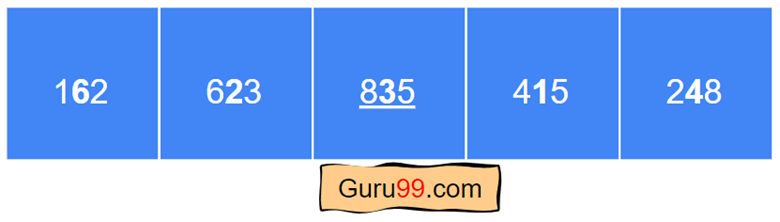
在本次迭代中,我们将考虑排序过程中的第 10 位数字。
第一步) 将整数除以 10。248 除以 10 得到 24。
第二步) 将第一步的输出取模 10。24 mod 10 得到 4。
第三步) 重复前一次迭代中的第二步。
第二次迭代后,列表现在看起来像这样
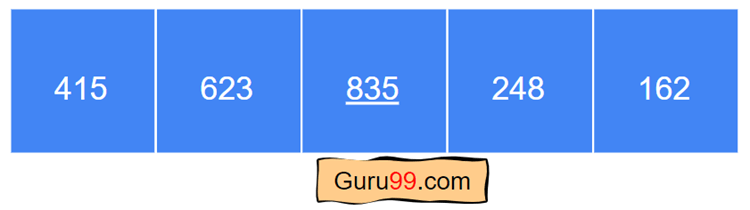
从上图可以看出,列表仍未完全排序,因为它尚未按升序排列。
c) 第三次迭代
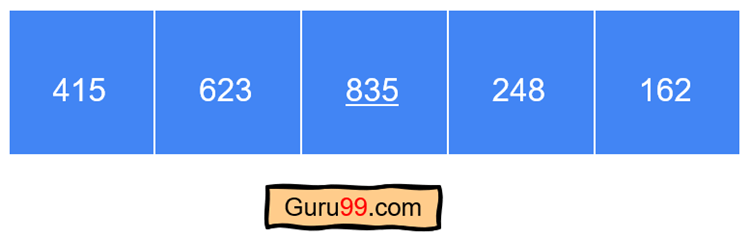
对于最后一次迭代,我们需要获得最高有效数字。在本例中,它是列表中每个整数的第 100 位。
第一步) 将整数除以 100……415 除以 100 得到 4。
第二步) 将第一步的结果取模 10。4 mod 10 再次得到 4。
第三步) 重复前一次迭代中的第三步。
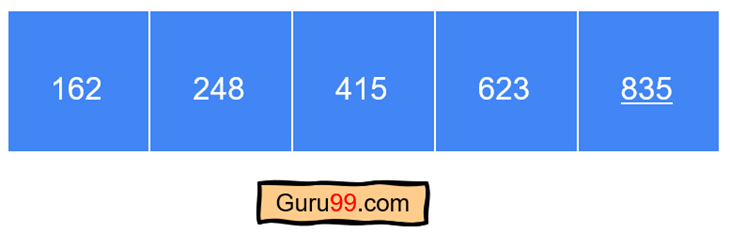
正如我们所见,列表现在已按升序排序。最后一次迭代已完成,排序过程现已结束。
基数排序算法的伪代码
这是基数排序算法的伪代码
radixSortAlgo(arr as an array) Find the largest element in arr maximum=the element in arr that is the largest Find the number of digits in maximum k=the number of digits in maximum Create buckets of size 0-9 k times for j -> 0 to k Acquire the jth place of each element in arr. Here j=0 represents the least significant digit. Use a stable sorting algorithm like counting sort to sort the elements in arr according to the digits of the elements in the jthplace arr = sorted elements
C++ 实现基数排序的程序
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
// Function to get the largest element in an array
int getMaximum(int arr[], int n) {
int maximum = arr[0];
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
if (maximum < arr[i]) maximum = arr[i];
}
return maximum;
}
// We are using counting sort to sort the elements digit by digit
void countingSortAlgo(int arr[], int size, int position) {
const int limit = 10;
int result[size];
int count[limit] = {0};
// Calculating the count of each integers
for (int j = 0; j < size; j++) count[(arr[j] / position) % 10]++;
// Calculating the cumulative count
for (int j = 1; j < limit; j++) {
count[j] += count[j - 1];
}
// Sort the integers
for (int j = size - 1; j >= 0; j--) {
result[count[(arr[j] / position) % 10] - 1] = arr[j];
count[(arr[j] / position) % 10]--;
}
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) arr[i] = result[i];
}
// The radixSort algorithm
void radixSortAlgo(int arr[], int size) {
// Get the largest element in the array
int maximum = getMaximum(arr, size);
for (int position = 1; maximum / position > 0; position *= 10)
countingSortAlgo(arr, size, position);
}
// Printing final result
void printResult(int arr[], int size) {
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
cout << arr[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
int main() {
int arr[] = {162, 623, 835, 415, 248};
int size = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
radixSortAlgo(arr, size);
printResult(arr, size);
}
输出
162 248 415 623 835
Python 实现基数排序算法的程序
#Radix Sort using python
def countingSortAlgo(arr, position):
n = len(arr)
result = [0] * n
count = [0] * 10 # Calculating the count of elements in the array arr
for j in range(0, n):
element = arr[j] // position
count[element % 10] += 1 # Calculating the cumulative count
for j in range(1, 10):
count[j] += count[j - 1] # Sorting the elements
i = n - 1
while i >= 0:
element = arr[i] // position
result[count[element % 10] - 1] = arr[i]
count[element % 10] -= 1
i -= 1
for j in range(0, n):
arr[j] = result[j]
def radixSortAlgo(arr): # Acquiring the largest element in the array
maximum = max(arr) # Using counting sort to sort digit by digit
position = 1
while maximum // position > 0:
countingSortAlgo(arr, position)
position *= 10
input = [162, 623, 835, 415, 248]
radixSortAlgo(input)
print(input)
输出
[162,248,415,623,835]
基数排序的复杂性分析
有两个复杂度需要考虑:空间复杂度和时间复杂度。
- 空间复杂度:O(n+b),其中 n 是数组的大小,b 是考虑的基数。
- 时间复杂度:O(d*(n+b)),其中 d 是数组中最大元素的位数。
基数排序的空间复杂度
空间复杂度需要关注的两个特征
- 数组中的元素数量,n。
- 表示元素的基数,b。
有时这个基数可能大于数组的大小。
因此,总复杂度为 O(n+b)。
列表中元素的以下属性可能会使基数排序的空间效率低下
- 具有大量数字的元素。
- 元素的基数很大,例如 64 位数字。
基数排序的时间复杂度
您可以使用计数排序作为子例程,因为每次迭代需要O(n+b) 时间。如果存在 d 次迭代,则总运行时间为O(d*(n+b))。此处,“O”表示复杂度函数。
基数排序的线性性
当以下情况发生时,基数排序是线性的
- d 是常数,其中 d 是数组中最大元素的位数。
- b 不会比 n 大很多。
基数排序与其他比较算法的比较
正如我们所见,基数排序的复杂性基于字或数字的大小。对于平均情况和最佳情况,其复杂度相同。即 O(d*(n+b))。此外,它还会根据您在中间使用的排序技术而有所不同。例如,您可以在基数排序内部使用计数排序或快速排序作为中间排序算法。
基数排序算法的应用
基数排序的重要应用是
- 基数排序可用作位置查找算法,用于处理大范围的值。
- 它用于 DC3 算法中构建后缀数组。
- 它在典型的计算机中的顺序、随机访问机器中用于带键的记录。
