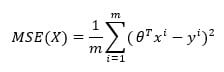使用 TensorFlow 的线性回归教程 [示例]
什么是线性回归?
线性回归是一种统计方法,用于模拟两个变量之间的关系。这种建模是在一个标量响应和一个或多个解释变量之间进行的。与一个解释变量的关系称为简单线性回归,而具有一个以上解释变量的关系称为多元线性回归。
TensorFlow 提供了工具来完全控制计算。这是通过低级 API 完成的。在此基础上,TensorFlow 配备了各种 API 来执行许多机器学习算法。这是高级 API。TensorFlow 将它们称为估计器
- 低级 API:从头开始构建模型架构和优化。对于初学者来说很复杂
- 高级 API:定义算法。它对用户更友好。TensorFlow 提供了一个名为估计器的工具箱来构建、训练、评估和进行预测。
在本教程中,您将仅使用估计器。计算速度更快,并且更易于实现。教程的第一部分解释了如何使用梯度下降优化器在 TensorFlow 中训练线性回归。在第二部分中,您将使用波士顿数据集通过 TensorFlow 估计器预测房屋价格。
如何训练线性回归模型
在我们开始训练模型之前,让我们先看看什么是线性回归。
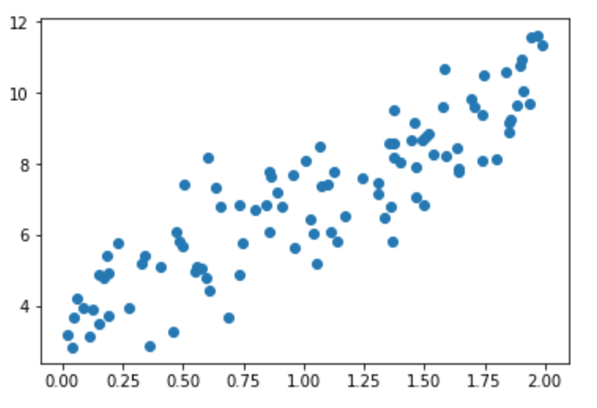
想象一下您有两个变量,x 和 y,您的任务是在知道 x 的值的情况下预测 y 的值。如果您绘制数据,您会看到自变量 x 和因变量 y 之间存在正相关关系。
您可能会注意到,如果 x=1,y 大约等于 6;如果 x=2,y 大约等于 8.5。
这不是一种非常准确的方法,并且容易出错,尤其是在拥有数十万个数据点的数据集上。
线性回归通过一个方程进行评估。变量 y 由一个或多个协变量解释。在您的示例中,只有一个因变量。如果要写出此方程,它将是
其中
是偏差。即,如果 x=0,y=
是与 x 相关的权重
是残差或模型的误差。它包括模型无法从数据中学到的内容
想象一下您拟合了模型,并找到了以下解
= 3.8
= 2.78
您可以将这些数字代入方程,得到
y= 3.8 + 2.78x
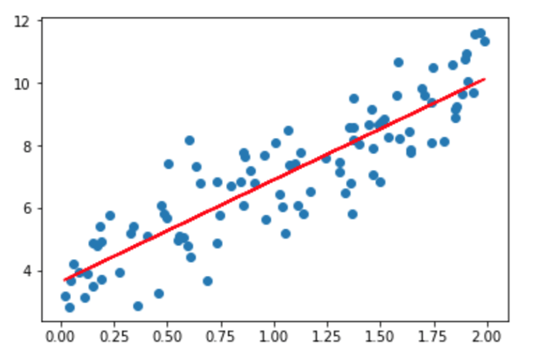
现在您有了一种更好的方法来查找 y 的值。也就是说,您可以将 x 替换为任何您想要预测 y 的值。在下图所示,我们将 x 替换为数据集中所有值,并绘制结果。
红线代表拟合值,即每个 x 值的 y 值。您无需查看 x 的值即可预测 y,对于每个 x 都有一个属于红线的值。您也可以预测大于 2 的 x 值!
如果您想将线性回归扩展到更多的协变量,您可以通过向模型添加更多变量来实现。传统分析与线性回归的区别在于,线性回归关注 y 如何对每个自变量 x 做出反应。
让我们看一个例子。想象一下您想预测一家冰淇淋店的销售额。数据集包含各种信息,例如天气(例如下雨、晴天、多云)、客户信息(例如薪水、性别、婚姻状况)。
传统分析将尝试通过计算每个变量的平均值来预测销售额,并尝试估计不同场景下的销售额。这将导致预测不佳,并将分析限制在选定的场景。
如果您使用线性回归,您可以写出这个方程
算法将找到权重的最佳解决方案;这意味着它将尝试最小化成本(拟合线与数据点之间的差异)。
算法如何工作
算法将为每个选择一个随机数和
并替换 x 的值以获得 y 的预测值。如果数据集有 100 个观测值,算法将计算 100 个预测值。
我们可以计算误差,表示为模型的误差,即预测值与真实值之间的差异。正误差表示模型低估了 y 的预测值,负误差表示模型高估了 y 的预测值。
您的目标是最小化误差的平方。算法计算平均误差平方。此步骤称为误差最小化。对于线性回归,它是均方误差,也称为 MSE。数学上,它是
Where
是权重,所以
表示预测值
- y 是真实值
- m 是观测值的数量
请注意,表示它使用矩阵的转置。
是均值的数学表示。
目标是找到最佳来最小化 MSE
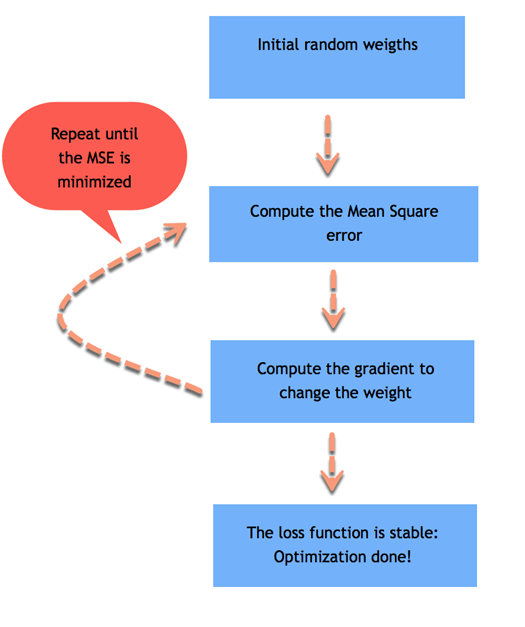
如果平均误差很大,则表示模型性能不佳,权重选择不当。要校正权重,您需要使用优化器。传统的优化器称为梯度下降。
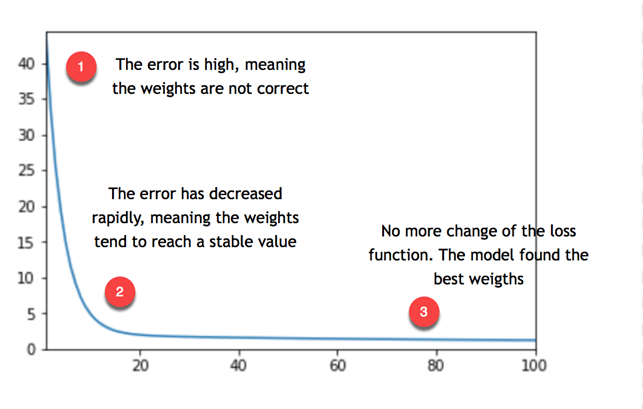
梯度下降取导数并增加或减少权重。如果导数为正,则权重减小。如果导数为负,则权重增加。模型将更新权重并重新计算误差。此过程重复进行,直到误差不再改变。每个过程称为一个迭代。此外,梯度乘以学习率。它表示学习的速度。
如果学习率太小,算法将需要很长时间才能收敛(即需要大量迭代)。如果学习率太高,算法可能永远无法收敛。
从上图可以看出,模型重复该过程约 20 次,然后找到权重的稳定值,从而达到最低误差。
请注意,误差不等于零,但稳定在 5 左右。这意味着模型会产生典型的 5 误差。如果您想减小误差,您需要向模型添加更多信息,例如更多变量或使用不同的估计器。
您还记得第一个方程
最终权重是 3.8 和 2.78。下面的视频向您展示了梯度下降如何优化损失函数以找到这些权重
如何使用 TensorFlow 训练线性回归
现在您对幕后发生了什么有了更好的了解,您可以使用 TensorFlow 提供的估计器 API 来训练您的第一个 TensorFlow 线性回归。
您将使用波士顿数据集,其中包含以下变量
| crim | 每个城镇的人均犯罪率 |
|---|---|
| zn | 面积超过 25,000 平方英尺的住宅用地比例。 |
| indus | 每个城镇非零售商业地产的比例。 |
| nox | 硝酸氧化物浓度 |
| rm | 每户平均房间数 |
| age | 1940 年前建造的自住单位比例 |
| dis | 到波士顿五个就业中心的加权距离 |
| tax | 每万美元的全部房产税率 |
| ptratio | 每个城镇的师生比例 |
| medv | 自住房屋的中位数价值(以千美元为单位) |
您将创建三个不同的数据集
| 数据集 | 目标 | 形状 |
|---|---|---|
| 训练 | 训练模型并获得权重 | 400, 10 |
| 评估 | 评估模型在未见过的数据上的性能 | 100, 10 |
| 预测 | 使用模型预测新数据上的房价 | 6, 10 |
目标是利用数据集的特征来预测房屋的价值。
在本教程的第二部分中,您将学习如何使用 TensorFlow 通过三种不同的方式导入数据
- 使用 Pandas
- 使用Numpy
- 仅 TF
请注意,所有选项结果相同。
您将学习如何使用高级 API 来构建、训练和评估 TensorFlow 线性回归模型。如果您使用的是低级 API,您将不得不手动定义
- 损失函数
- 优化器:梯度下降
- 矩阵乘法
- 图和张量
这对于初学者来说很繁琐且更复杂。
Pandas
您需要导入必要的库来训练模型。
import pandas as pd from sklearn import datasets import tensorflow as tf import itertools
第 1 步)使用 Pandas 导入数据。
您定义列名并将其存储在 COLUMNS 中。您可以使用 pd.read_csv() 导入数据。
COLUMNS = ["crim", "zn", "indus", "nox", "rm", "age",
"dis", "tax", "ptratio", "medv"]
training_set = pd.read_csv(“E:/boston_train.csv”, skipinitialspace=True,skiprows=1, names=COLUMNS)
test_set = pd.read_csv(“E:/boston_test.csv”, skipinitialspace=True,skiprows=1, names=COLUMNS)
prediction_set = pd.read_csv(“E:/boston_predict.csv”, skipinitialspace=True,skiprows=1, names=COLUMNS)
您可以打印数据的形状。
print(training_set.shape, test_set.shape, prediction_set.shape)
输出
(400, 10) (100, 10) (6, 10)
请注意,标签,即您的 y,已包含在数据集中。所以您需要定义另外两个列表。一个只包含特征,一个只包含标签的名称。这两个列表将告诉您的估计器数据中的特征是什么,以及标签的列名是什么
它是使用以下代码完成的。
FEATURES = ["crim", "zn", "indus", "nox", "rm",
"age", "dis", "tax", "ptratio"]
LABEL = "medv"
第 2 步)转换数据
您需要将数字变量转换为正确的格式。TensorFlow 提供了一种转换连续变量的方法:tf.feature_column.numeric_column()。
在之前的步骤中,您定义了一个您想包含在模型中的特征列表。现在您可以使用此列表将它们转换为数字数据。如果您想在模型中排除特征,请在构造 feature_cols 之前随意删除一个或多个变量 FEATURES 列表
请注意,您将使用 Python 列表推导式和 FEATURES 列表来创建一个名为 feature_cols 的新列表。它有助于您避免九次编写 tf.feature_column.numeric_column()。列表推导式是一种更快、更简洁的新列表创建方法
feature_cols = [tf.feature_column.numeric_column(k) for k in FEATURES]
第 3 步)定义估计器
在此步骤中,您需要定义估计器。TensorFlow 目前提供了 6 个预构建的估计器,包括 3 个用于分类任务和 3 个用于 TensorFlow 回归任务
- 回归器
- DNNRegressor
- LinearRegressor
- DNNLineaCombinedRegressor
- 分类器
- DNNClassifier
- LinearClassifier
- DNNLineaCombinedClassifier
在本教程中,您将使用 Linear Regressor。要访问此功能,您需要使用 tf.estimator。
该函数需要两个参数
- feature_columns:包含要包含在模型中的变量
- model_dir:存储图、保存模型参数等的路径
TensorFlow 将在您的工作目录中自动创建一个名为 train 的文件。您需要使用此路径来访问 Tensorboard,如下面的 TensorFlow 回归示例所示。
estimator = tf.estimator.LinearRegressor(
feature_columns=feature_cols,
model_dir="train")
输出
INFO:tensorflow:Using default config.
INFO:tensorflow:Using config: {'_model_dir': 'train', '_tf_random_seed': None, '_save_summary_steps': 100, '_save_checkpoints_steps': None, '_save_checkpoints_secs': 600, '_session_config': None, '_keep_checkpoint_max': 5, '_keep_checkpoint_every_n_hours': 10000, '_log_step_count_steps': 100, '_train_distribute': None, '_service': None, '_cluster_spec': <tensorflow.python.training.server_lib.ClusterSpec object at 0x1a215dc550>, '_task_type': 'worker', '_task_id': 0, '_global_id_in_cluster': 0, '_master': '', '_evaluation_master': '', '_is_chief': True, '_num_ps_replicas': 0, '_num_worker_replicas': 1}
TensorFlow 的棘手之处在于为模型提供数据的方式。TensorFlow 设计用于并行计算和非常大的数据集。由于机器资源的限制,不可能一次将所有数据输入模型。为此,您需要每次输入一批数据。请注意,我们讨论的是拥有数百万甚至更多记录的巨大数据集。如果您不添加批处理,您最终会遇到内存错误。
例如,如果您的数据包含 100 个观测值,并且您定义了一个批次大小为 10,则表示模型在每次迭代中会看到 10 个观测值(10*10)。
当模型看到所有数据后,它完成一个epoch。Epoch 定义了您希望模型查看数据的次数。最好将此步骤设置为 none,让模型执行指定次数的迭代。
第二个要添加的信息是您是否想在每次迭代前对数据进行洗牌。在训练过程中,洗牌数据很重要,这样模型就不会学习数据集的特定模式。如果模型学习了数据底层模式的细节,它将在泛化预测未见过的数据时遇到困难。这称为过拟合。模型在训练数据上表现良好,但无法正确预测未见过的数据。
TensorFlow 使这两个步骤变得容易。当数据进入管道时,它会知道需要多少观测值(批次)以及是否需要洗牌数据。
要指示 TensorFlow 如何为模型提供数据,您可以使用 pandas_input_fn。此对象需要 5 个参数
- x:特征数据
- y:标签数据
- batch_size:批次大小。默认为 128
- num_epoch:Epoch 数量,默认为 1
- shuffle:是否洗牌数据。默认为 None
您需要多次向模型提供数据,因此您需要定义一个函数来重复此过程。所有这些函数 get_input_fn。
def get_input_fn(data_set, num_epochs=None, n_batch = 128, shuffle=True):
return tf.estimator.inputs.pandas_input_fn(
x=pd.DataFrame({k: data_set[k].values for k in FEATURES}),
y = pd.Series(data_set[LABEL].values),
batch_size=n_batch,
num_epochs=num_epochs,
shuffle=shuffle)
评估模型性能的常用方法是
- 训练模型
- 在不同的数据集上评估模型
- 进行预测
TensorFlow 估计器提供了三个不同的函数来轻松完成这三个步骤。
第 4 步):训练模型
您可以使用估计器的 train 来评估模型。train 估计器需要一个 input_fn 和一个迭代次数。您可以使用上面创建的函数为模型提供数据。然后,您指示模型迭代 1000 次。请注意,您没有指定 epoch 的数量,而是让模型迭代 1000 次。如果您将 epoch 设置为 1,那么模型将迭代 4 次:训练集有 400 条记录,批次大小为 128
- 128 行
- 128 行
- 128 行
- 16 行
因此,最好将 epoch 设置为 none 并定义迭代次数,如下面的 TensorFlow 分类示例所示。
estimator.train(input_fn=get_input_fn(training_set,
num_epochs=None,
n_batch = 128,
shuffle=False),
steps=1000)
输出
INFO:tensorflow:Calling model_fn. INFO:tensorflow:Done calling model_fn. INFO:tensorflow:Create CheckpointSaverHook. INFO:tensorflow:Graph was finalized. INFO:tensorflow:Running local_init_op. INFO:tensorflow:Done running local_init_op. INFO:tensorflow:Saving checkpoints for 1 into train/model.ckpt. INFO:tensorflow:loss = 83729.64, step = 1 INFO:tensorflow:global_step/sec: 238.616 INFO:tensorflow:loss = 13909.657, step = 101 (0.420 sec) INFO:tensorflow:global_step/sec: 314.293 INFO:tensorflow:loss = 12881.449, step = 201 (0.320 sec) INFO:tensorflow:global_step/sec: 303.863 INFO:tensorflow:loss = 12391.541, step = 301 (0.327 sec) INFO:tensorflow:global_step/sec: 308.782 INFO:tensorflow:loss = 12050.5625, step = 401 (0.326 sec) INFO:tensorflow:global_step/sec: 244.969 INFO:tensorflow:loss = 11766.134, step = 501 (0.407 sec) INFO:tensorflow:global_step/sec: 155.966 INFO:tensorflow:loss = 11509.922, step = 601 (0.641 sec) INFO:tensorflow:global_step/sec: 263.256 INFO:tensorflow:loss = 11272.889, step = 701 (0.379 sec) INFO:tensorflow:global_step/sec: 254.112 INFO:tensorflow:loss = 11051.9795, step = 801 (0.396 sec) INFO:tensorflow:global_step/sec: 292.405 INFO:tensorflow:loss = 10845.855, step = 901 (0.341 sec) INFO:tensorflow:Saving checkpoints for 1000 into train/model.ckpt. INFO:tensorflow:Loss for final step: 5925.9873.
您可以使用以下命令检查 Tensorboard
activate hello-tf # For MacOS tensorboard --logdir=./train # For Windows tensorboard --logdir=train
第 5 步)评估您的模型
您可以使用以下代码评估模型在测试集上的拟合度
ev = estimator.evaluate(
input_fn=get_input_fn(test_set,
num_epochs=1,
n_batch = 128,
shuffle=False))
输出
INFO:tensorflow:Calling model_fn. INFO:tensorflow:Done calling model_fn. INFO:tensorflow:Starting evaluation at 2018-05-13-01:43:13 INFO:tensorflow:Graph was finalized. INFO:tensorflow:Restoring parameters from train/model.ckpt-1000 INFO:tensorflow:Running local_init_op. INFO:tensorflow:Done running local_init_op. INFO:tensorflow:Finished evaluation at 2018-05-13-01:43:13 INFO:tensorflow:Saving dict for global step 1000: average_loss = 32.15896, global_step = 1000, loss = 3215.896
您可以使用以下代码打印损失
loss_score = ev["loss"]
print("Loss: {0:f}".format(loss_score))
输出
Loss: 3215.895996
模型损失为 3215。您可以查看摘要统计信息以了解误差的大小。
training_set['medv'].describe()
输出
count 400.000000 mean 22.625500 std 9.572593 min 5.000000 25% 16.600000 50% 21.400000 75% 25.025000 max 50.000000 Name: medv, dtype: float64
从上面的摘要统计中,您知道房屋的平均价格是 22 千美元,最低价格是 9 千美元,最高价格是 50 千美元。该模型产生的典型误差为 3k 美元。
第 6 步)进行预测
最后,您可以使用 TensorFlow 的 predict 估计器来估计 6 栋波士顿房屋的价值。
y = estimator.predict(
input_fn=get_input_fn(prediction_set,
num_epochs=1,
n_batch = 128,
shuffle=False))
要打印的估计值,您可以使用此代码
predictions = list(p["predictions"] for p in itertools.islice(y, 6))print("Predictions: {}".format(str(predictions)))
输出
INFO:tensorflow:Calling model_fn. INFO:tensorflow:Done calling model_fn. INFO:tensorflow:Graph was finalized. INFO:tensorflow:Restoring parameters from train/model.ckpt-1000 INFO:tensorflow:Running local_init_op. INFO:tensorflow:Done running local_init_op. Predictions: [array([32.297546], dtype=float32), array([18.96125], dtype=float32), array([27.270979], dtype=float32), array([29.299236], dtype=float32), array([16.436684], dtype=float32), array([21.460876], dtype=float32)]
模型预测了以下值
| 房屋 | 预测 | |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 32.29 | |
| 2 | 18.96 | |
| 3 | 27.27 | |
| 4 | 29.29 | |
| 5 | 16.43 | |
| 7 | 21.46 |
请注意,我们不知道真实值。在深度学习教程中,您将尝试击败线性模型
Numpy 解决方案
本节介绍如何使用 numpy 估计器来馈送数据来训练模型。方法相同,只是您将使用 numpy_input_fn 估计器。
training_set_n = pd.read_csv(“E:/boston_train.csv”).values
test_set_n = pd.read_csv(“E:/boston_test.csv”).values
prediction_set_n = pd.read_csv(“E:/boston_predict.csv”).values
第 1 步)导入数据
首先,您需要区分特征变量和标签。您需要对训练数据和评估数据执行此操作。定义一个函数来分割数据会更快。
def prepare_data(df):
X_train = df[:, :-3]
y_train = df[:,-3]
return X_train, y_train
您可以使用该函数从训练/评估数据集中分割标签和特征
X_train, y_train = prepare_data(training_set_n) X_test, y_test = prepare_data(test_set_n)
您需要排除预测数据集的最后一列,因为它只包含 NaN
x_predict = prediction_set_n[:, :-2]
确认数组的形状。请注意,标签不应具有维度,它意味着(400,)。
print(X_train.shape, y_train.shape, x_predict.shape)
输出
(400, 9) (400,) (6, 9)
您可以按以下方式构建特征列
feature_columns = [ tf.feature_column.numeric_column('x', shape=X_train.shape[1:])]
估计器定义如前所述,您指示特征列和存储图的位置。
estimator = tf.estimator.LinearRegressor(
feature_columns=feature_columns,
model_dir="train1")
输出
INFO:tensorflow:Using default config.
INFO:tensorflow:Using config: {'_model_dir': 'train1', '_tf_random_seed': None, '_save_summary_steps': 100, '_save_checkpoints_steps': None, '_save_checkpoints_secs': 600, '_session_config': None, '_keep_checkpoint_max': 5, '_keep_checkpoint_every_n_hours': 10000, '_log_step_count_steps': 100, '_train_distribute': None, '_service': None, '_cluster_spec': <tensorflow.python.training.server_lib.ClusterSpec object at 0x1a218d8f28>, '_task_type': 'worker', '_task_id': 0, '_global_id_in_cluster': 0, '_master': '', '_evaluation_master': '', '_is_chief': True, '_num_ps_replicas': 0, '_num_worker_replicas': 1}
您可以使用 numpy 估计器将数据馈送到模型,然后训练模型。请注意,我们之前定义了 input_fn 函数以方便阅读。
# Train the estimatortrain_input = tf.estimator.inputs.numpy_input_fn(
x={"x": X_train},
y=y_train,
batch_size=128,
shuffle=False,
num_epochs=None)
estimator.train(input_fn = train_input,steps=5000)
输出
INFO:tensorflow:Calling model_fn. INFO:tensorflow:Done calling model_fn. INFO:tensorflow:Create CheckpointSaverHook. INFO:tensorflow:Graph was finalized. INFO:tensorflow:Running local_init_op. INFO:tensorflow:Done running local_init_op. INFO:tensorflow:Saving checkpoints for 1 into train1/model.ckpt. INFO:tensorflow:loss = 83729.64, step = 1 INFO:tensorflow:global_step/sec: 490.057 INFO:tensorflow:loss = 13909.656, step = 101 (0.206 sec) INFO:tensorflow:global_step/sec: 788.986 INFO:tensorflow:loss = 12881.45, step = 201 (0.126 sec) INFO:tensorflow:global_step/sec: 736.339 INFO:tensorflow:loss = 12391.541, step = 301 (0.136 sec) INFO:tensorflow:global_step/sec: 383.305 INFO:tensorflow:loss = 12050.561, step = 401 (0.260 sec) INFO:tensorflow:global_step/sec: 859.832 INFO:tensorflow:loss = 11766.133, step = 501 (0.117 sec) INFO:tensorflow:global_step/sec: 804.394 INFO:tensorflow:loss = 11509.918, step = 601 (0.125 sec) INFO:tensorflow:global_step/sec: 753.059 INFO:tensorflow:loss = 11272.891, step = 701 (0.134 sec) INFO:tensorflow:global_step/sec: 402.165 INFO:tensorflow:loss = 11051.979, step = 801 (0.248 sec) INFO:tensorflow:global_step/sec: 344.022 INFO:tensorflow:loss = 10845.854, step = 901 (0.288 sec) INFO:tensorflow:Saving checkpoints for 1000 into train1/model.ckpt. INFO:tensorflow:Loss for final step: 5925.985. Out[23]: <tensorflow.python.estimator.canned.linear.LinearRegressor at 0x1a1b6ea860>
您使用不同的估计器重复相同的步骤来评估您的模型
eval_input = tf.estimator.inputs.numpy_input_fn(
x={"x": X_test},
y=y_test,
shuffle=False,
batch_size=128,
num_epochs=1)
estimator.evaluate(eval_input,steps=None)
输出
INFO:tensorflow:Calling model_fn.
INFO:tensorflow:Done calling model_fn.
INFO:tensorflow:Starting evaluation at 2018-05-13-01:44:00
INFO:tensorflow:Graph was finalized.
INFO:tensorflow:Restoring parameters from train1/model.ckpt-1000
INFO:tensorflow:Running local_init_op.
INFO:tensorflow:Done running local_init_op.
INFO:tensorflow:Finished evaluation at 2018-05-13-01:44:00
INFO:tensorflow:Saving dict for global step 1000: average_loss = 32.158947, global_step = 1000, loss = 3215.8945
Out[24]:
{'average_loss': 32.158947, 'global_step': 1000, 'loss': 3215.8945}
最后,您可以计算预测。它应该与 Pandas 相似。
test_input = tf.estimator.inputs.numpy_input_fn(
x={"x": x_predict},
batch_size=128,
num_epochs=1,
shuffle=False)
y = estimator.predict(test_input)
predictions = list(p["predictions"] for p in itertools.islice(y, 6))
print("Predictions: {}".format(str(predictions)))
输出
INFO:tensorflow:Calling model_fn. INFO:tensorflow:Done calling model_fn. INFO:tensorflow:Graph was finalized. INFO:tensorflow:Restoring parameters from train1/model.ckpt-1000 INFO:tensorflow:Running local_init_op. INFO:tensorflow:Done running local_init_op. Predictions: [array([32.297546], dtype=float32), array([18.961248], dtype=float32), array([27.270979], dtype=float32), array([29.299242], dtype=float32), array([16.43668], dtype=float32), array([21.460878], dtype=float32)]
Tensorflow 解决方案
最后一节是关于 TensorFlow 解决方案的。此方法比其他方法稍微复杂一些。
请注意,如果您使用Jupyter notebook,您需要重启并清理内核才能运行此会话。
TensorFlow 构建了一个强大的工具来将数据传入管道。在本节中,您将自行构建 input_fn 函数。
第 1 步)定义数据的路径和格式
首先,您声明两个变量,其中包含 csv 文件的路径。请注意,您有两个文件,一个用于训练集,一个用于测试集。
import tensorflow as tf
df_train = "E:/boston_train.csv"
df_eval = "E:/boston_test.csv"
然后,您需要定义要从 csv 文件使用的列。我们将使用所有列。之后,您需要声明它是哪种类型的变量。
浮点变量定义为 [0.]
COLUMNS = ["crim", "zn", "indus", "nox", "rm", "age",
"dis", "tax", "ptratio", "medv"]RECORDS_ALL = [[0.0], [0.0], [0.0], [0.0],[0.0],[0.0],[0.0],[0.0],[0.0],[0.0]]
第 2 步)定义 input_fn 函数
该函数可以分为三个部分
- 导入数据
- 创建迭代器
- 消耗数据
以下是定义函数的整体代码。代码将在之后进行解释
def input_fn(data_file, batch_size, num_epoch = None):
# Step 1
def parse_csv(value):
columns = tf.decode_csv(value, record_defaults= RECORDS_ALL)
features = dict(zip(COLUMNS, columns))
#labels = features.pop('median_house_value')
labels = features.pop('medv')
return features, labels
# Extract lines from input files using the
Dataset API. dataset = (tf.data.TextLineDataset(data_file) # Read text file
.skip(1) # Skip header row
.map(parse_csv))
dataset = dataset.repeat(num_epoch)
dataset = dataset.batch(batch_size)
# Step 3
iterator = dataset.make_one_shot_iterator()
features, labels = iterator.get_next()
return features, labels
**导入数据**
对于 csv 文件,dataset 方法一次读取一行。要构建数据集,您需要使用 TextLineDataset 对象。您的数据集有标题,所以您需要使用 skip(1) 来跳过第一行。此时,您只读取数据并排除管道中的标题。为了馈送模型,您需要将特征与标签分开。用于对数据应用任何转换的方法是 map。
此方法调用您将创建的函数来指示如何转换数据。简而言之,您需要将数据传入 TextLineDataset 对象,排除标题,并应用由函数指示的转换。代码解释
- tf.data.TextLineDataset(data_file):此行读取 csv 文件
- .skip(1) :跳过标题
- .map(parse_csv)):将记录解析为张量您需要定义一个函数来指示 map 对象。您可以将此函数调用为 parse_csv。
此函数使用 tf.decode_csv 方法解析 csv 文件,并声明特征和标签。特征可以声明为字典或元组。您使用字典方法,因为它更方便。代码解释
- tf.decode_csv(value, record_defaults= RECORDS_ALL):decode_csv 方法使用 TextLineDataset 的输出来读取 csv 文件。record_defaults 指示 TensorFlow 关于列类型。
- dict(zip(_CSV_COLUMNS, columns)):使用在此数据处理期间提取的所有列填充字典
- features.pop(‘median_house_value’): 从特征变量中排除目标变量并创建标签变量
Dataset 需要更多元素来迭代地馈送 Tensors。事实上,您需要添加 repeat 方法以允许数据集无限期地继续馈送模型。如果您不添加该方法,模型将只迭代一次然后抛出错误,因为没有更多数据馈送到管道中。
之后,您可以通过 batch 方法控制批次大小。这意味着您告诉数据集每次迭代您想在管道中传递多少数据。如果您设置了较大的批次大小,模型将会变慢。
第 3 步)创建迭代器
现在您已准备好进行第二步:创建一个迭代器来返回数据集中的元素。
创建操作员的最简单方法是使用 make_one_shot_iterator 方法。
之后,您可以从迭代器创建特征和标签。
第 4 步)消耗数据
您可以在会话中调用该函数来消耗数据。您可以尝试将批次大小设置为 1。
请注意,它将特征以字典形式打印,并将标签以数组形式打印。
它将显示 csv 文件的第一行。您可以尝试多次运行此代码并使用不同的批次大小。
next_batch = input_fn(df_train, batch_size = 1, num_epoch = None)
with tf.Session() as sess:
first_batch = sess.run(next_batch)
print(first_batch)
输出
({'crim': array([2.3004], dtype=float32), 'zn': array([0.], dtype=float32), 'indus': array([19.58], dtype=float32), 'nox': array([0.605], dtype=float32), 'rm': array([6.319], dtype=float32), 'age': array([96.1], dtype=float32), 'dis': array([2.1], dtype=float32), 'tax': array([403.], dtype=float32), 'ptratio': array([14.7], dtype=float32)}, array([23.8], dtype=float32))
第 4 步)定义特征列
您需要按如下方式定义数字列
X1= tf.feature_column.numeric_column('crim')
X2= tf.feature_column.numeric_column('zn')
X3= tf.feature_column.numeric_column('indus')
X4= tf.feature_column.numeric_column('nox')
X5= tf.feature_column.numeric_column('rm')
X6= tf.feature_column.numeric_column('age')
X7= tf.feature_column.numeric_column('dis')
X8= tf.feature_column.numeric_column('tax')
X9= tf.feature_column.numeric_column('ptratio')
请注意,您需要将所有变量组合到一个存储桶中
base_columns = [X1, X2, X3,X4, X5, X6,X7, X8, X9]
第 5 步)构建模型
您可以使用 estimator LinearRegressor 来训练模型。
model = tf.estimator.LinearRegressor(feature_columns=base_columns, model_dir='train3')
输出
INFO:tensorflow:Using default config. INFO:tensorflow:Using config: {'_model_dir': 'train3', '_tf_random_seed': None, '_save_summary_steps': 100, '_save_checkpoints_steps': None, '_save_checkpoints_secs': 600, '_session_config': None, '_keep_checkpoint_max': 5, '_keep_checkpoint_every_n_hours': 10000, '_log_step_count_steps': 100, '_train_distribute': None, '_service': None, '_cluster_spec': <tensorflow.python.training.server_lib.ClusterSpec object at 0x1820a010f0>, '_task_type': 'worker', '_task_id': 0, '_global_id_in_cluster': 0, '_master': '', '_evaluation_master': '', '_is_chief': True, '_num_ps_replicas': 0, '_num_worker_replicas': 1}
您需要使用 lambda 函数来允许在 input_fn 函数中编写参数。如果您不使用 lambda 函数,您将无法训练模型。
# Train the estimatormodel.train(steps =1000,
input_fn= lambda : input_fn(df_train,batch_size=128, num_epoch = None))
输出
INFO:tensorflow:Calling model_fn. INFO:tensorflow:Done calling model_fn. INFO:tensorflow:Create CheckpointSaverHook. INFO:tensorflow:Graph was finalized. INFO:tensorflow:Running local_init_op. INFO:tensorflow:Done running local_init_op. INFO:tensorflow:Saving checkpoints for 1 into train3/model.ckpt. INFO:tensorflow:loss = 83729.64, step = 1 INFO:tensorflow:global_step/sec: 72.5646 INFO:tensorflow:loss = 13909.657, step = 101 (1.380 sec) INFO:tensorflow:global_step/sec: 101.355 INFO:tensorflow:loss = 12881.449, step = 201 (0.986 sec) INFO:tensorflow:global_step/sec: 109.293 INFO:tensorflow:loss = 12391.541, step = 301 (0.915 sec) INFO:tensorflow:global_step/sec: 102.235 INFO:tensorflow:loss = 12050.5625, step = 401 (0.978 sec) INFO:tensorflow:global_step/sec: 104.656 INFO:tensorflow:loss = 11766.134, step = 501 (0.956 sec) INFO:tensorflow:global_step/sec: 106.697 INFO:tensorflow:loss = 11509.922, step = 601 (0.938 sec) INFO:tensorflow:global_step/sec: 118.454 INFO:tensorflow:loss = 11272.889, step = 701 (0.844 sec) INFO:tensorflow:global_step/sec: 114.947 INFO:tensorflow:loss = 11051.9795, step = 801 (0.870 sec) INFO:tensorflow:global_step/sec: 111.484 INFO:tensorflow:loss = 10845.855, step = 901 (0.897 sec) INFO:tensorflow:Saving checkpoints for 1000 into train3/model.ckpt. INFO:tensorflow:Loss for final step: 5925.9873. Out[8]: <tensorflow.python.estimator.canned.linear.LinearRegressor at 0x18225eb8d0>
您可以使用以下代码评估模型在测试集上的拟合度
results = model.evaluate(steps =None,input_fn=lambda: input_fn(df_eval, batch_size =128, num_epoch = 1))
for key in results:
print(" {}, was: {}".format(key, results[key]))
输出
INFO:tensorflow:Calling model_fn. INFO:tensorflow:Done calling model_fn. INFO:tensorflow:Starting evaluation at 2018-05-13-02:06:02 INFO:tensorflow:Graph was finalized. INFO:tensorflow:Restoring parameters from train3/model.ckpt-1000 INFO:tensorflow:Running local_init_op. INFO:tensorflow:Done running local_init_op. INFO:tensorflow:Finished evaluation at 2018-05-13-02:06:02 INFO:tensorflow:Saving dict for global step 1000: average_loss = 32.15896, global_step = 1000, loss = 3215.896 average_loss, was: 32.158958435058594 loss, was: 3215.89599609375 global_step, was: 1000
最后一步是根据值预测值,即特征的矩阵。您可以编写一个包含您想要预测的值的字典。您的模型有 9 个特征,所以您需要为每个特征提供一个值。模型将为每个特征提供一个预测。
在下面的代码中,您编写了 df_predict csv 文件中包含的每个特征的值。
您需要编写一个新的 input_fn 函数,因为数据集中没有标签。您可以使用 Dataset 的 from_tensor API。
prediction_input = {
'crim': [0.03359,5.09017,0.12650,0.05515,8.15174,0.24522],
'zn': [75.0,0.0,25.0,33.0,0.0,0.0],
'indus': [2.95,18.10,5.13,2.18,18.10,9.90],
'nox': [0.428,0.713,0.453,0.472,0.700,0.544],
'rm': [7.024,6.297,6.762,7.236,5.390,5.782],
'age': [15.8,91.8,43.4,41.1,98.9,71.7],
'dis': [5.4011,2.3682,7.9809,4.0220,1.7281,4.0317],
'tax': [252,666,284,222,666,304],
'ptratio': [18.3,20.2,19.7,18.4,20.2,18.4]
}
def test_input_fn():
dataset = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensors(prediction_input)
return dataset
# Predict all our prediction_inputpred_results = model.predict(input_fn=test_input_fn)
最后,您将打印预测结果。
for pred in enumerate(pred_results): print(pred)
输出
INFO:tensorflow:Calling model_fn.
INFO:tensorflow:Done calling model_fn.
INFO:tensorflow:Graph was finalized.
INFO:tensorflow:Restoring parameters from train3/model.ckpt-1000
INFO:tensorflow:Running local_init_op.
INFO:tensorflow:Done running local_init_op.
(0, {'predictions': array([32.297546], dtype=float32)})
(1, {'predictions': array([18.96125], dtype=float32)})
(2, {'predictions': array([27.270979], dtype=float32)})
(3, {'predictions': array([29.299236], dtype=float32)})
(4, {'predictions': array([16.436684], dtype=float32)})
(5, {'predictions': array([21.460876], dtype=float32)})
INFO:tensorflow:Calling model_fn. INFO:tensorflow:Done calling model_fn. INFO:tensorflow:Graph was finalized. INFO:tensorflow:Restoring parameters from train3/model.ckpt-5000 INFO:tensorflow:Running local_init_op. INFO:tensorflow:Done running local_init_op. (0, {'predictions': array([35.60663], dtype=float32)}) (1, {'predictions': array([22.298521], dtype=float32)}) (2, {'predictions': array([25.74533], dtype=float32)}) (3, {'predictions': array([35.126694], dtype=float32)}) (4, {'predictions': array([17.94416], dtype=float32)}) (5, {'predictions': array([22.606628], dtype=float32)})
摘要
要训练模型,您需要
- 定义特征:自变量:X
- 定义标签:因变量:y
- 构建训练/测试集
- 定义初始权重
- 定义损失函数:MSE
- 优化模型:梯度下降
- 定义
- 学习率
- Epoch 数量
- 批次大小
在本教程中,您学习了如何为线性回归 TensorFlow 估计器使用高级 API。您需要定义
- 特征列。如果是连续的:tf.feature_column.numeric_column()。您可以使用 Python 列表推导式填充列表
- 估计器:tf.estimator.LinearRegressor(feature_columns, model_dir)
- 用于导入数据、批次大小和 epoch 的函数:input_fn()
之后,您就可以使用 train()、evaluate() 和 predict() 来训练、评估和预测了。