Python break、continue、pass 语句及示例
循环的概念几乎存在于所有编程语言中。Python 循环有助于遍历列表、元组、字符串、字典和集合。Python 支持两种类型的循环:“for” 和 “while”。循环内的代码块会重复执行,直到条件不满足为止。
循环控制语句会中断执行流程,并根据我们的需要终止/跳过迭代。Python 中的 break 和 continue 语句在循环内部使用,以改变循环的正常执行流程。
for-loop 或 while-loop 旨在迭代直到给定的条件不满足为止。当您使用 break 或 continue 语句时,循环的流程会偏离正常方式。
Python break 语句
break 语句负责终止其所在的循环。如果 break 语句用于嵌套循环中,则会终止当前循环,并将流程继续执行循环之后的代码。
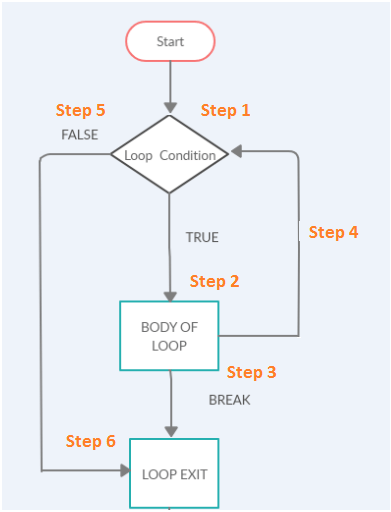
break 语句的流程图如下
流程图涉及以下步骤。
步骤 1) 循环开始执行。
步骤 2) 如果循环条件为真,它将执行步骤 2,即执行循环体。
步骤 3) 如果循环体中包含 break 语句,循环将退出并转到步骤 6。
步骤 4) 循环条件执行完毕后,将进入步骤 4 的下一次迭代。
步骤 5) 如果循环条件为假,它将退出循环并转到步骤 6。
步骤 6) 循环结束。
Break 语句执行流程
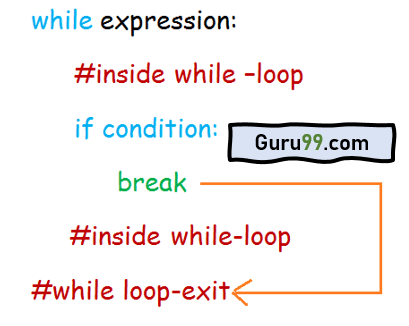
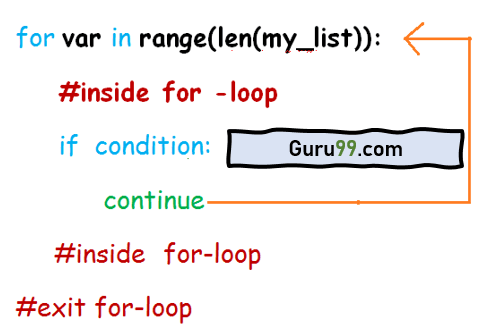
当 for-loop 开始执行时,它会检查 if-condition。如果为真,则执行 break 语句,for-loop 将终止。如果条件为假,则执行 for-loop 中的代码。
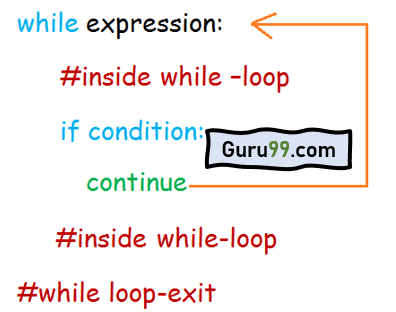
当 while 循环执行时,它会检查 if-condition;如果为真,则执行 break 语句,while-loop 将退出。如果 if 条件为假,则执行 while-loop 中的代码。
示例:for-loop 中的 Break 语句
列表 my_list = [‘Siya’, ‘Tiya’, ‘Guru’, ‘Daksh’, ‘Riya’, ‘Guru’] 使用 for-loop 进行循环。我们有兴趣从列表 my_list 中搜索名称“Guru”。
在 for-loop 中,if-condition 将列表中的每个项与名称“Guru”进行比较。如果条件为真,将执行 break 语句,循环将终止。
使用 break 语句的工作示例如下所示
my_list = ['Siya', 'Tiya', 'Guru', 'Daksh', 'Riya', 'Guru']
for i in range(len(my_list)):
print(my_list[i])
if my_list[i] == 'Guru':
print('Found the name Guru')
break
print('After break statement')
print('Loop is Terminated')
预期输出
Siya Tiya Guru Found the name Guru Loop is Terminated
示例:while-loop 中的 Break 语句
my_list = ['Siya', 'Tiya', 'Guru', 'Daksh', 'Riya', 'Guru']
i = 0
while True:
print(my_list[i])
if (my_list[i] == 'Guru'):
print('Found the name Guru')
break
print('After break statement')
i += 1
print('After while-loop exit')
预期输出
Siya Tiya Guru Found name Guru After while-loop exit
示例:嵌套循环中的 Break 语句
在此示例中,我们有两个 for-loop。两个 for-loop 都从 0 到 3 的范围进行迭代。在第二个 for-loop 中,我们添加了一个条件,即如果第二个 for-loop 索引的值为 2,则应中断。
因此,由于 break 语句,第二个 for-loop 永远不会迭代 2 和 3。
for i in range(4):
for j in range(4):
if j==2:
break
print("The number is ",i,j);
预期输出
The number is 0 0 The number is 0 1 The number is 1 0 The number is 1 1 The number is 2 0 The number is 2 1 The number is 3 0 The number is 3 1
Python continue 语句
continue 语句会跳过其后的代码,并将控制权交还给循环的开头,以进行下一次迭代。
语法
continue
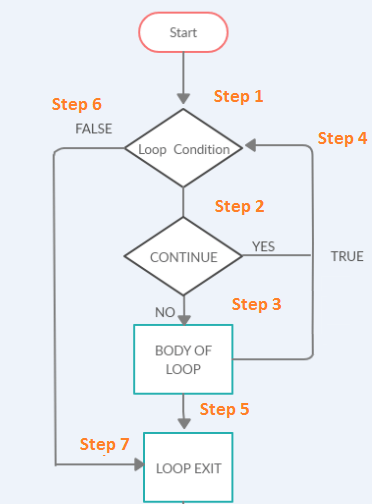
Continue 流程图
流程图涉及以下步骤。
步骤 1) 循环开始执行。
步骤 2) 将执行循环内的代码。如果循环中有 continue 语句,控制权将返回到步骤 4,即循环的开头,以进行下一次迭代。
步骤 3) 将执行循环内的代码。
步骤 4) 如果存在 continue 语句或循环体内的循环执行完成,它将调用下一次迭代。
步骤 5) 循环执行完成后,循环将退出并转到步骤 7。
步骤 6) 如果步骤 1 中的循环条件不满足,它将退出循环并转到步骤 7。
步骤 7) 循环结束。
Continue 语句执行流程
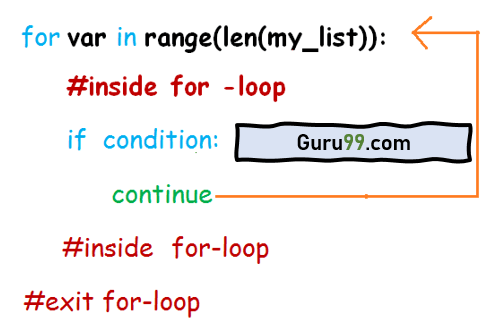
for-loop 遍历给定的 my_list 数组。在 for-loop 中,if-condition 被执行。如果条件为真,则执行 continue 语句,控制权将传递到循环的开头以进行下一次迭代。
代码流程如下所示
当 while 循环执行时,它会检查 if-condition,如果为真,则执行 continue 语句。控制权将返回到 while-loop 的开头以进行下一次迭代。如果 if 条件为假,则执行 while-loop 中的代码。
代码流程如下所示
示例:for-loop 中的 Continue
for i in range(10):
if i == 7:
continue
print("The Number is :" , i)
预期输出
The Number is : 0 The Number is : 1 The Number is : 2 The Number is : 3 The Number is : 4 The Number is : 5 The Number is : 6 The Number is : 8 The Number is : 9
示例:while-loop 中的 Continue
i = 0
while i <= 10:
if i == 7:
i += 1
continue
print("The Number is :" , i)
i += 1
预期输出
The Number is : 0 The Number is : 1 The Number is : 2 The Number is : 3 The Number is : 4 The Number is : 5 The Number is : 6 The Number is : 8 The Number is : 9 The Number is : 10
示例:嵌套循环中的 Continue
下面的示例展示了使用两个 for-loop。两个 for-loop 都从 0 到 3 的范围进行迭代。在第二个 for-loop 中,有一个条件,即如果第二个 for-loop 索引的值为 2,则应继续。因此,由于continue语句,第二个 for-loop 将跳过 2 的迭代并继续到 3。
for i in range(4):
for j in range(4):
if j==2:
continue
print("The number is ",i,j);
预期输出
The number is 0 0 The number is 0 1 The number is 0 3 The number is 1 0 The number is 1 1 The number is 1 3 The number is 2 0 The number is 2 1 The number is 2 3 The number is 3 0 The number is 3 1 The number is 3 3
Python pass 语句
Python pass 语句用作循环、函数、类、if 语句中的占位符,这些将在以后实现。
语法
pass
Python 中的 pass 语句是什么?
Python pass 是一个空语句。当 Python 解释器遇到 pass 语句时,它什么也不做,并被忽略。
何时使用 pass 语句?
假设您有一个函数或类,其主体为空。您计划将来编写代码。如果 Python 解释器遇到空主体,它将抛出错误。
也可以在函数或类的正文中添加注释,但解释器会忽略注释并抛出错误。
pass 语句可以用于函数或类正文中。在执行期间,解释器遇到 pass 语句时,会忽略它并继续执行,而不会引发任何错误。
示例:函数中的 pass 语句
在此示例中,pass 被添加到函数中。调用函数时将执行它,如下所示
def my_func():
print('pass inside function')
pass
my_func()
预期输出
pass inside function
示例:类中的 pass 语句
在下面的示例中,我们创建了一个空类,其中包含一个 print 语句,后跟一个 pass 语句。pass 语句表示“My_Class”类中的代码将在将来实现。
classMy_Class:
print("Inside My_Class")
pass
输出
Inside My_Class
示例:循环中的 pass 语句
在下面的示例中,字符串“Guru”在 for-loop 中使用。if-condition 检查字符“r”,然后调用 print 语句后跟 pass。
# Pass statement in for-loop
test = "Guru"
for i in test:
if i == 'r':
print('Pass executed')
pass
print(i)
预期输出
G u Pass executed r u
示例:if 语句中的 pass 语句
在此示例中,if 语句检查 a 的值,如果条件为真,则打印“pass executed”语句,后跟 pass。
a=1
if a==1:
print('pass executed')
pass
预期输出
pass executed
何时使用 break 和 continue 语句?
- break 语句在循环中使用时,将终止循环并退出。如果用于嵌套循环中,它将跳出当前循环。
- continue 语句在循环中使用时会停止当前执行,并将控制权返回到循环的开头。
break 和 continue 语句的主要区别在于,当遇到 break 关键字时,它将退出循环。
在 continue 关键字的情况下,当前正在运行的迭代将停止,并继续进行下一次迭代。
摘要
- Python break 和 continue 语句用于循环内部,以改变循环的正常执行流程。
- 一个 for-loop 或 while-loop 旨在迭代直到给定的条件不满足为止。当您使用 break 或 continue 语句时,循环的流程会偏离正常方式。
- break 语句在循环中使用时,将终止循环并退出。如果用于嵌套循环中,它将跳出当前循环。
- continue 语句在循环中使用时,将停止当前执行,并将控制权返回到循环的开头。
- break 和 continue 语句的主要区别在于,当遇到 break 关键字时,它将退出循环。
- Python Pass 语句用作循环、函数、类、if 语句中的占位符,这些将在以后实现。
- Python pass 是一个空语句。当执行开始并且解释器遇到 pass 语句时,它什么也不做,并被忽略。