Python 条件语句:IF…Else、ELIF 和 Switch Case
Python 中的条件语句是什么?
Python 中的条件语句根据特定的布尔约束是求值为真还是假,执行不同的计算或操作。Python 中的 IF 语句处理条件语句。
什么是 Python If 语句?
Python If 语句用于决策制定操作。它包含一个代码块,仅当 if 语句中的条件为真时运行。如果条件为假,则运行可选的 else 语句,其中包含 else 条件的一些代码。
当您想证明一个条件而另一个条件不正确时,您可以使用 Python if else 语句。
Python if 语句语法
if expression Statement else Statement
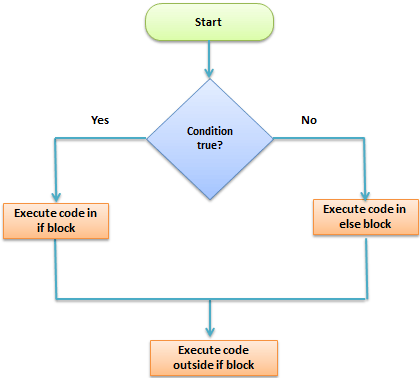
Python if…else 流程图
让我们看一个 Python if else 语句的例子
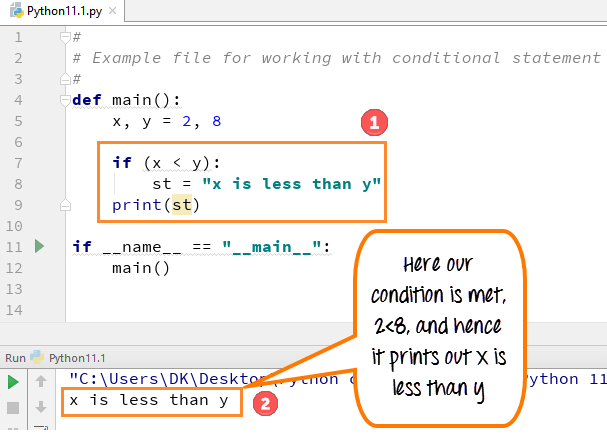
# #Example file for working with conditional statement # def main(): x,y =2,8 if(x < y): st= "x is less than y" print(st) if __name__ == "__main__": main()
- 第 5 行代码:我们定义了两个变量 x, y = 2, 8
- 第 7 行代码:Python 中的 if 语句检查条件 x<y,在此情况下为真
- 第 8 行代码:变量 st 被设置为“x 小于 y。”
- 第 9 行代码:print st 行将输出变量 st 的值,“x 小于 y”,
当“if 条件”不满足时会发生什么
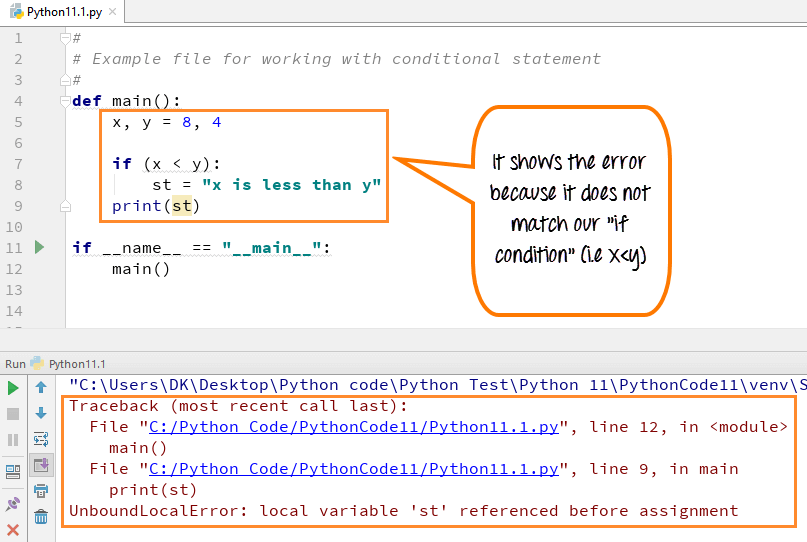
在此步骤中,我们将看到当 Python 中的 if 条件不满足时会发生什么。
- 第 5 行代码:我们定义了两个变量 x, y = 8, 4
- 第 7 行代码:Python 中的 if 语句检查条件 x<y,在此情况下为假
- 第 8 行代码:变量 st **未**设置为“x 小于 y。”
- 第 9 行代码:print st 行 – 试图打印一个从未声明过的变量的值。因此,我们得到一个错误。
如何使用“else 条件”
“else 条件”通常用于当您需要根据其他语句来判断一个语句时。如果一个条件出错了,那么应该有另一个条件来证明该语句或逻辑。
示例:
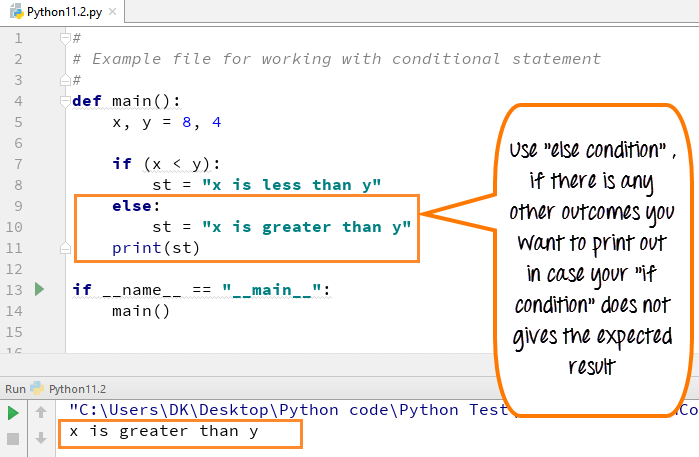
# #Example file for working with conditional statement # def main(): x,y =8,4 if(x < y): st= "x is less than y" else: st= "x is greater than y" print (st) if __name__ == "__main__": main()
- 第 5 行代码:我们定义了两个变量 x, y = 8, 4
- 第 7 行代码:Python 中的 if 语句检查条件 x<y,在此情况下为假
- 第 9 行代码:程序控制流转到 else 条件
- 第 10 行代码:变量 st 被设置为“x大于 y。”
- 第 11 行代码:print st 行将输出变量 st 的值,“x 大于 y”,
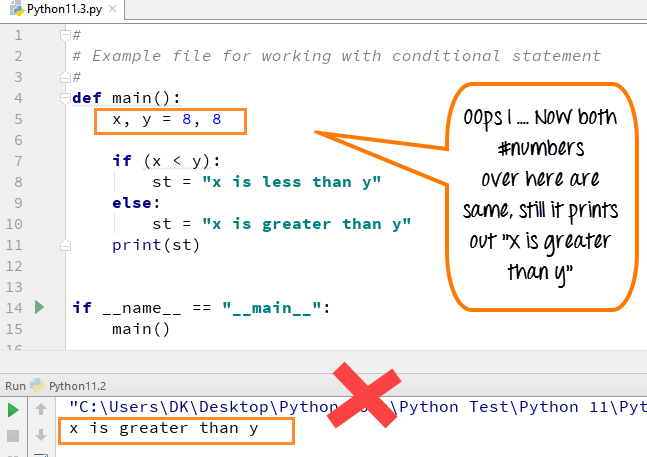
当“else 条件”不起作用时
在许多情况下,您的“else 条件”可能无法为您提供所需的结果。它会打印出错误的结果,因为程序逻辑有误。在大多数情况下,当您需要在程序中证明两个以上的语句或条件时,就会发生这种情况。
一个示例将更好地帮助您理解这个概念。
在这里,两个变量都是相同的 (8,8),程序输出为“x 大于 y”,这是错误的。这是因为它会检查第一个条件(Python 中的 if 条件),如果失败,它将默认打印第二个条件(else 条件)。在下一步中,我们将看到如何纠正此错误。
# #Example file for working with conditional statement # def main(): x,y =8,8 if(x < y): st= "x is less than y" else: st= "x is greater than y" print(st) if __name__ == "__main__": main()
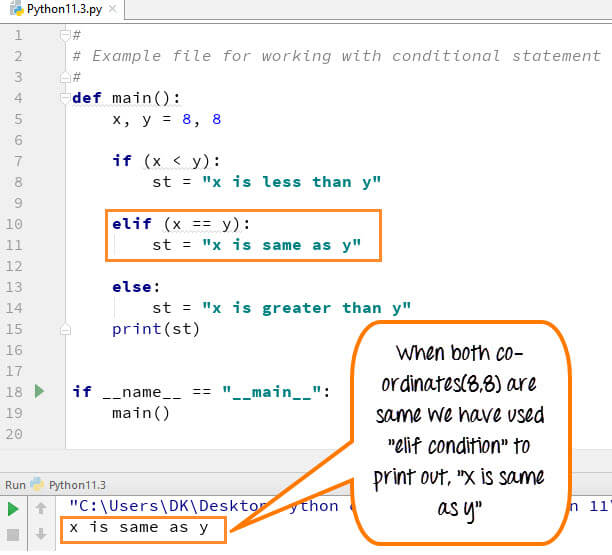
如何使用“elif”条件
为了纠正“else 条件”先前的错误,我们可以使用“elif”语句。通过使用“elif”条件,您是在告诉程序在其他条件出错或不正确时打印第三个条件或可能性。
示例
# #Example file for working with conditional statement # def main(): x,y =8,8 if(x < y): st= "x is less than y" elif (x == y): st= "x is same as y" else: st="x is greater than y" print(st) if __name__ == "__main__": main()
- 第 5 行代码:我们定义了两个变量 x, y = 8, 8
- 第 7 行代码:If 语句检查条件 x<y,在此情况下为假
- 第 10 行代码:程序控制流转到 elseif 条件。它检查 x==y 是否为真
- 第 11 行代码:变量 st 被设置为“x等于 y。”
- 第 15 行代码:程序控制流退出 If 语句(不会到达 else 语句)。 并打印变量 st。输出是“x 等于 y”,这是正确的
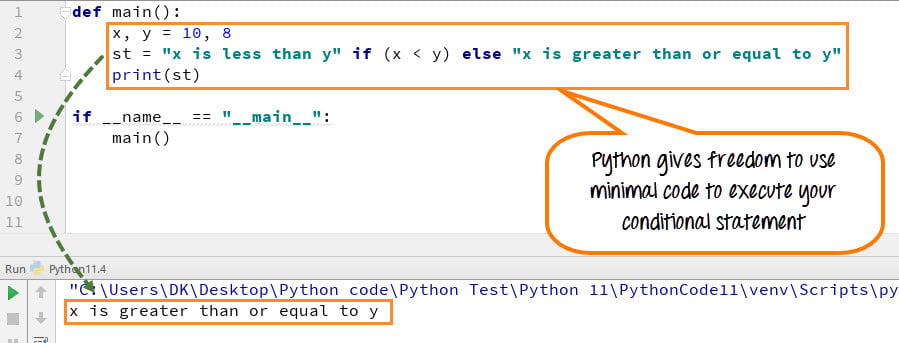
如何用最少的代码执行条件语句
在此步骤中,我们将看到如何精简条件语句。我们可以将它们与单个代码一起使用,而不是单独执行每个条件的代码。
语法
A If B else C
示例:
def main(): x,y = 10,8 st = "x is less than y" if (x < y) else "x is greater than or equal to y" print(st) if __name__ == "__main__": main()
- 第 2 行代码:我们定义了两个变量 x, y = 10, 8
- 第 3 行代码:如果 x<y,则变量 st 被设置为“x 小于 y”,否则它被设置为“x 大于或等于 y”。在此 x>y 中,变量 st 被设置为“x 大于或等于 y。”
- 第 4 行代码:打印 st 的值并给出正确的输出
-
Python 允许您以简短简洁的方式编写代码,而不是为条件语句编写冗长的代码。
Python 嵌套 if 语句
下面的示例演示了 Python 嵌套 if 语句
total = 100
#country = "US"
country = "AU"
if country == "US":
if total <= 50:
print("Shipping Cost is $50")
elif total <= 100:
print("Shipping Cost is $25")
elif total <= 150:
print("Shipping Costs $5")
else:
print("FREE")
if country == "AU":
if total <= 50:
print("Shipping Cost is $100")
else:
print("FREE")
取消注释上面代码的第 2 行,注释第 3 行并再次运行代码
Python 中的 Switch Case 语句
什么是 Switch 语句?
Switch 语句是一种多路分支语句,它将变量的值与 case 语句中指定的值进行比较。
Python 语言没有 switch 语句。
Python使用字典映射在 Python 中实现 Switch Case
示例
function(argument){
switch(argument) {
case 0:
return "This is Case Zero";
case 1:
return " This is Case One";
case 2:
return " This is Case Two ";
default:
return "nothing";
};
};
对于上面的 Python Switch case
def SwitchExample(argument):
switcher = {
0: " This is Case Zero ",
1: " This is Case One ",
2: " This is Case Two ",
}
return switcher.get(argument, "nothing")
if __name__ == "__main__":
argument = 1
print (SwitchExample(argument))
Python 2 示例
以上代码是 Python 3 示例,如果您想在 Python 2 中运行,请参考以下代码。
# If Statement
#Example file for working with conditional statement
#
def main():
x,y =2,8
if(x < y):
st= "x is less than y"
print st
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
# How to use "else condition"
#Example file for working with conditional statement
#
def main():
x,y =8,4
if(x < y):
st= "x is less than y"
else:
st= "x is greater than y"
print st
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
# When "else condition" does not work
#Example file for working with conditional statement
#
def main():
x,y =8,8
if(x < y):
st= "x is less than y"
else:
st= "x is greater than y"
print st
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
# How to use "elif" condition
#Example file for working with conditional statement
#
def main():
x,y =8,8
if(x < y):
st= "x is less than y"
elif (x == y):
st= "x is same as y"
else:
st="x is greater than y"
print st
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
# How to execute conditional statement with minimal code
def main():
x,y = 10,8
st = "x is less than y" if (x < y) else "x is greater than or equal to y"
print st
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
# Nested IF Statement
total = 100
#country = "US"
country = "AU"
if country == "US":
if total <= 50:
print "Shipping Cost is $50"
elif total <= 100:
print "Shipping Cost is $25"
elif total <= 150:
print "Shipping Costs $5"
else:
print "FREE"
if country == "AU":
if total <= 50:
print "Shipping Cost is $100"
else:
print "FREE"
#Switch Statement
def SwitchExample(argument):
switcher = {
0: " This is Case Zero ",
1: " This is Case One ",
2: " This is Case Two ",
}
return switcher.get(argument, "nothing")
if __name__ == "__main__":
argument = 1
print SwitchExample(argument)
摘要
Python 中的条件语句由 if 语句处理,我们在这里看到了其他几种使用条件语句的方式,例如 Python if else。
- “if 条件”——当您需要在一个或多个条件为真或假时打印结果时使用它。
- “else 条件”——当您的一个条件未能满足要求时,您想打印语句时使用它
- “elif 条件”——当您有第三种可能性作为结果时使用它。您可以使用多个 elif 条件来检查代码中的第 4、5、6 种可能性
- 我们可以使用最少的代码来执行条件语句,方法是将所有条件声明为单个语句以运行代码
- Python If 语句可以嵌套