HBase 查询示例:HBase 中的 put()、get()、scan() 命令
将数据写入HBase表:Shell
put 命令用于将数据存储到表中
Syntax: put <'tablename'>,<'rowname'>,<'columnvalue'>,<'value'>
此命令用于以下事项
- 它将在已定义或指定的表、行或列中放置一个单元格“值”。
- 它将可选地协调时间戳。
示例
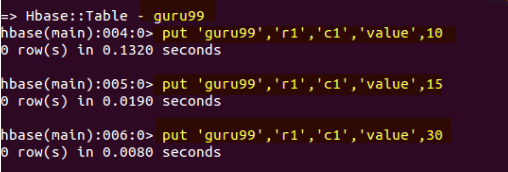
- 在此,我们将值放入名为“guru99”的表中,位于行 r1 和列 c1 下
hbase> put 'guru99', 'r1', 'c1', 'value', 10
- 我们已将三个值 10、15 和 30 放入名为“guru99”的表中,如下图所示
- 假设名为“Guru99”的表有一些表引用,例如 g。我们也可以在表引用上运行命令,例如
hbase> g.put 'guru99', 'r1', 'c1', 'value', 10
- 在插入值到“guru99”后,输出将如上图所示。
从HBase表中读取数据:Shell
在本节中,我们将检查以下内容
- 插入到 HBase 表“guru99”中的值
- HBase 表 guru99 中存在的带有值的列名
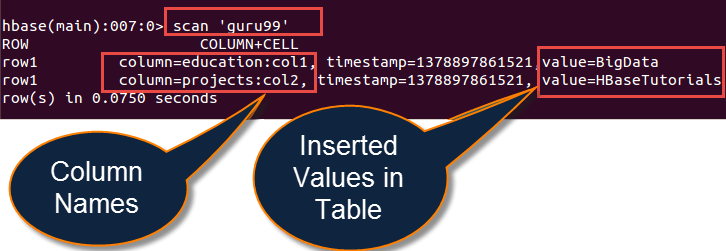
从上图,我们可以推断
- 如果在 HBase shell 中运行“scan”命令,它将按如下方式显示“guru99”中的插入值
- 在 HBase shell 中,它将显示我们代码插入的值以及列名和行名
- 这里我们可以看到插入的列名是“education”和“projects”
- 插入的值是“大数据”和“HBase 教程”到指定列
您还可以使用 Get 命令从表中读取数据
Syntax: get <'tablename'>, <'rowname'>, {< Additional parameters>}
此处“
使用此命令,您将获得表中存在的行或单元格内容。此外,您还可以添加其他参数,如 TIMESTAMP、TIMERANGE、VERSIONS、FILTERS 等,以获取特定的行或单元格内容。
例子:-
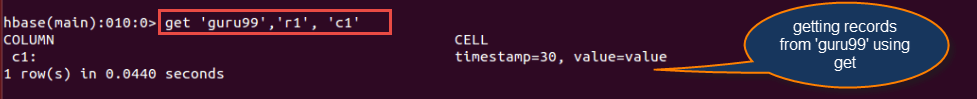
hbase> get 'guru99', 'r1', {COLUMN => 'c1'}
对于表“guru99”,行 r1 和列 c1 的值将使用此命令显示,如上图所示
hbase> get 'guru99', 'r1'
对于表“guru99”,行 r1 的值将使用此命令显示
hbase> get 'guru99', 'r1', {TIMERANGE => [ts1, ts2]}
对于表“guru99”,行 1 在时间范围 ts1 和 ts2 的值将使用此命令显示
hbase> get 'guru99', 'r1', {COLUMN => ['c1', 'c2', 'c3']}
对于表“guru99”,行 r1 和列族 c1、c2、c3 的值将使用此命令显示
将数据写入HBase表:JAVA API
在此步骤中,我们将把数据写入 HBase 表“guru99”
首先,我们必须使用 -HBaseLoading.java 程序编写用于插入和检索 HBase 值的代码。
要创建表并在列级别插入值,您需要像这样编写代码.
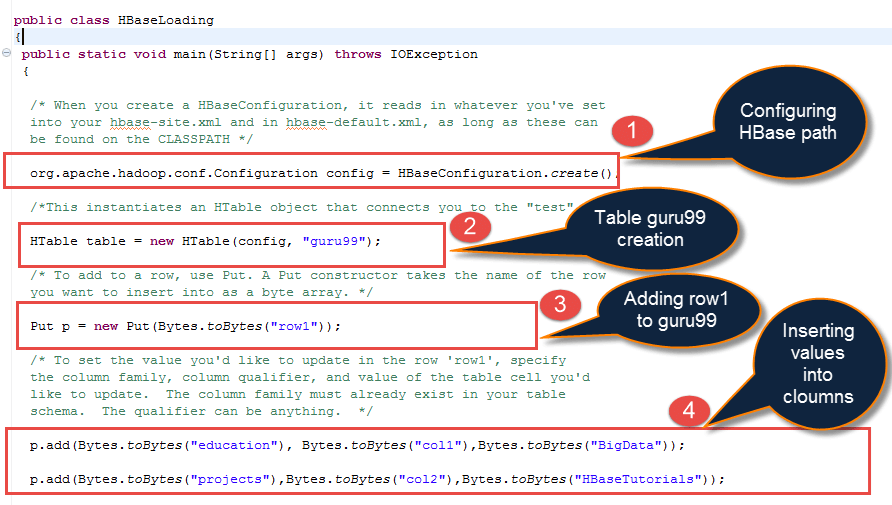
从上面的屏幕截图
- 当我们创建 HBase 配置时,它将指向我们在 HBase 安装过程中在 base-site.xml 和 hbase-default.xml 文件中设置的所有配置
- 使用 HTable 方法创建表“guru99”
- 向表“guru99”添加行1
- 指定列名“education”和“projects”,并将值插入到行1的相应列名中。此处插入的值是“BigData”和“HBaseTutorials”。
从HBase表中读取数据:Java API
在上面的部分中,我们放入 HBase 表中的任何值,在这里我们将获取并显示这些值。
检索存储在“guru99”中的结果
上述屏幕截图显示数据正在从 HBase 表 'guru99' 中读取
- 在这里,我们将获取存储在列族中的值,即“education”和“projects”
- 使用“get”命令我们将获取 HBase 表中存储的值
- 使用“scan”命令扫描结果。存储在行1中的值将显示在控制台上。
编写代码完成后,您需要像这样运行 Java 应用程序
- 右键单击 HBaseLoading.java -> 运行方式 -> Java 应用程序
- 运行“HBaseLoading .java”后,值将插入到 HBase 中每个列的“guru99”中,并且在同一程序中也可以检索值。
这是完整的代码
import java.io.IOException;
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.HBaseConfiguration;
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.client.Get;
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.client.HTable;
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.client.Put;
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.client.Result;
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.client.ResultScanner;
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.client.Scan;
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.util.Bytes;
public class HBaseLoading
{
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException
{
/* When you create a HBaseConfiguration, it reads in whatever you've set into your hbase-site.xml and in hbase-default.xml, as long as these can be found on the CLASSPATH*/
org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration config = HBaseConfiguration.create();
/*This instantiates an HTable object that connects you to the "test" table*/
HTable table = new HTable(config, "guru99");
/* To add to a row, use Put. A Put constructor takes the name of the row you want to insert into as a byte array.*/
Put p = new Put(Bytes.toBytes("row1"));
/*To set the value you'd like to update in the row 'row1', specify the column family, column qualifier, and value of the table cell you'd like to update. The column family must already exist in your table schema. The qualifier can be anything.*/
p.add(Bytes.toBytes("education"), Bytes.toBytes("col1"),Bytes.toBytes("BigData"));
p.add(Bytes.toBytes("projects"),Bytes.toBytes("col2"),Bytes.toBytes("HBaseTutorials"));
// Once you've adorned your Put instance with all the updates you want to make, to commit it do the following
table.put(p);
// Now, to retrieve the data we just wrote.
Get g = new Get(Bytes.toBytes("row1"));
Result r = table.get(g);
byte [] value = r.getValue(Bytes.toBytes("education"),Bytes.toBytes("col1"));
byte [] value1 = r.getValue(Bytes.toBytes("projects"),Bytes.toBytes("col2"));
String valueStr = Bytes.toString(value);
String valueStr1 = Bytes.toString(value1);
System.out.println("GET: " +"education: "+ valueStr+"projects: "+valueStr1);
Scan s = new Scan();
s.addColumn(Bytes.toBytes("education"), Bytes.toBytes("col1"));
s.addColumn(Bytes.toBytes("projects"), Bytes.toBytes("col2"));
ResultScanner scanner = table.getScanner(s);
try
{
for (Result rr = scanner.next(); rr != null; rr = scanner.next())
{
System.out.println("Found row : " + rr);
}
} finally
{
// Make sure you close your scanners when you are done!
scanner.close();
}
}
}
摘要
正如我们在本教程中所讨论的,您可以使用 put 命令将数据插入表中。您可以使用 scan、get 命令从表中读取数据