Python 队列:FIFO、LIFO 示例
什么是 Python Queue?
队列是一个容器,用于存储数据。先进入的数据会先被移除,因此队列也称为“先进先出”(FIFO)。队列有两个端:前端和后端。项目从后端插入,从前端移除。
Python Queue 如何工作?
队列可以很容易地与现实世界的例子进行比较:在售票处排队的人群,第一个排队的人会先得到票,然后是下一个人,依此类推。队列数据结构也是如此。
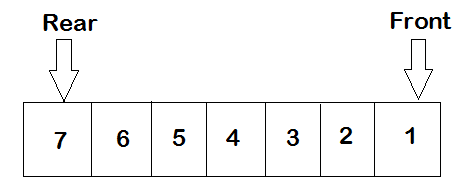
这是队列的图示表示
后端表示将项目插入队列的点。在此示例中,7 是值。
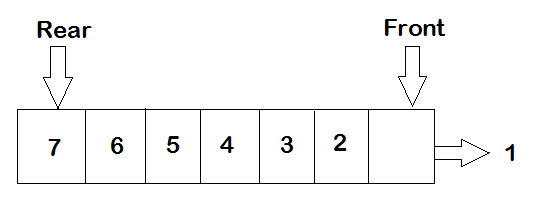
前端表示将从队列中移除项目的点。如果要从队列中移除项目,第一个得到的元素是 1,如图所示。
项目 1 是第一个被插入队列的项目,在移除时它是第一个出来的。因此,队列称为先进先出(FIFO)
在队列中,项目是按顺序移除的,不能从中间移除。您不能随意从队列中移除项目 5,要做到这一点,您必须移除 5 之前的所有项目。队列中的项目将按插入顺序移除。
Python 队列类型
Python 中主要有两种类型的队列
- 先进先出队列:对于这种队列,先进入的元素将先出来。要使用 FIFO,您必须从 queue 模块调用 **Queue()** 类。
- 后进先出队列:在这里,最后进入的元素将首先出来。要使用 LIFO,您必须从 queue 模块调用 **LifoQueue()** 类。
Python 队列安装
在 Python 中使用队列非常容易。以下是使队列在代码中使用的步骤:
步骤 1) 您只需要导入 queue 模块,如下所示
import queue
该模块默认随 Python 提供,您无需任何额外安装即可开始使用队列。队列有两种类型:FIFO(先进先出)和 LIFO(后进先出)。
步骤 2) 要使用 FIFO 队列,请调用导入的 queue 模块的 Queue 类,如下所示
import queue q1 = queue.Queue()
步骤 3) 要使用 LIFO 队列,请调用 LifoQueue() 类,如下所示
import queue q1 = queue.LifoQueue()
Queue 和 LifoQueue 类中可用的方法
以下是 Queue 和 LifoQueue 类中重要的可用方法
- put(item):这将把项目放入队列。
- get():这将从队列中返回一个项目。
- empty():如果队列为空,则返回 true;如果存在项目,则返回 false。
- qsize():返回队列的大小。
- full():如果队列已满,则返回 true;否则返回 false。
先进先出队列示例
在先进先出队列中,先进入的元素将先出来。
向队列添加项目
让我们通过一个示例来演示如何向队列添加项目。要开始使用队列,首先导入 queue 模块,如以下示例所示。
要添加项目,您可以使用 put() 方法,如示例所示
import queue q1 = queue.Queue() q1.put(10) #this will additem 10 to the queue.
默认情况下,队列的大小是无限的,您可以向其中添加任意数量的项目。如果您想定义队列的大小,可以这样做:
import queue q1 = queue.Queue(5) #The max size is 5. q1.put(1) q1.put(2) q1.put(3) q1.put(4) q1.put(5) print(q1.full()) # will return true.
输出
True
现在队列的大小是 5,它最多只能容纳 5 个项目,并且 q1.full() 方法将返回 true。添加更多项目将不会进一步执行代码。
从队列中移除项目
要从队列中移除项目,您可以使用 get() 方法。调用此方法时,它会允许从队列中移除项目。
以下示例显示了如何从队列中移除项目。
import queue
q1 = queue.Queue()
q1.put(10)
item1 = q1.get()
print('The item removed from the queue is ', item1)
输出
The item removed from the queue is 10
后进先出队列示例
在后进先出队列中,最后进入的元素将首先出来。
要使用 LIFO(后进先出)队列,我们需要导入 queue 模块并使用 LifoQueue() 方法。
向队列添加项目
在这里,我们将了解如何向 LIFO 队列添加项目。
import queue q1 = queue.LifoQueue() q1.put(10)
您必须在 LifoQueue 上使用 put() 方法,如上例所示。
从队列中移除项目
要从 LIFO 队列中移除项目,您可以使用 get() 方法。
import queue
q1 = queue.LifoQueue()
q1.put(10)
item1 = q1.get()
print('The item removed from the LIFO queue is ', item1)
输出
The item removed from the LIFO queue is 10
向队列添加多个项目
在上面的示例中,我们已经看到了如何为 FIFO 和 LIFO 队列添加单个项目和移除项目。现在我们将看到如何添加多个项目以及如何移除它们。
向 FIFO 队列添加项目
import queue
q1 = queue.Queue()
for i in range(20):
q1.put(i) # this will additem from 0 to 20 to the queue
从 FIFO 队列中移除项目
import queue
q1 = queue.Queue()
for i in range(20):
q1.put(i) # this will additem from 0 to 20 to the queue
while not q1.empty():
print("The value is ", q1.get()) # get() will remove the item from the queue.
输出
The value is 0 The value is 1 The value is 2 The value is 3 The value is 4 The value is 5 The value is 6 The value is 7 The value is 8 The value is 9 The value is 10 The value is 11 The value is 12 The value is 13 The value is 14 The value is 15 The value is 16 The value is 17 The value is 18 The value is 19
向 LIFO 队列添加项目
import queue
q1 = queue.LifoQueue()
for i in range(20):
q1.put(i) # this will additem from 0 to 20 to the queue
从 LIFO 队列中移除项目
import queue
q1 = queue.LifoQueue()
for i in range(20):
q1.put(i) # this will additem from 0 to 20 to the queue
while not q1.empty():
print("The value is ", q1.get()) # get() will remove the item from the queue.
输出
The value is 19 The value is 18 The value is 17 The value is 16 The value is 15 The value is 14 The value is 13 The value is 12 The value is 11 The value is 10 The value is 9 The value is 8 The value is 7 The value is 6 The value is 5 The value is 4 The value is 3 The value is 2 The value is 1 The value is 0
队列排序
以下示例显示了队列排序。用于排序的算法是冒泡排序。
import queue
q1 = queue.Queue()
#Addingitems to the queue
q1.put(11)
q1.put(5)
q1.put(4)
q1.put(21)
q1.put(3)
q1.put(10)
#using bubble sort on the queue
n = q1.qsize()
for i in range(n):
x = q1.get() # the element is removed
for j in range(n-1):
y = q1.get() # the element is removed
if x > y :
q1.put(y) #the smaller one is put at the start of the queue
else:
q1.put(x) # the smaller one is put at the start of the queue
x = y # the greater one is replaced with x and compared again with nextelement
q1.put(x)
while (q1.empty() == False):
print(q1.queue[0], end = " ")
q1.get()
输出
3 4 5 10 11 21
队列反转
要反转队列,您可以使用另一个队列和递归。
以下示例演示了如何反转队列。
示例
import queue
q1 = queue.Queue()
q1.put(11)
q1.put(5)
q1.put(4)
q1.put(21)
q1.put(3)
q1.put(10)
def reverseQueue (q1src, q2dest) :
buffer = q1src.get()
if (q1src.empty() == False) :
reverseQueue(q1src, q2dest) #using recursion
q2dest.put(buffer)
return q2dest
q2dest = queue.Queue()
qReversed = reverseQueue(q1,q2dest)
while (qReversed.empty() == False):
print(qReversed.queue[0], end = " ")
qReversed.get()
输出
10 3 21 4 5 11
摘要
- 队列是一个容器,用于存储数据。队列有两种类型:FIFO 和 LIFO。
- 对于 FIFO(先进先出队列),先进入的元素将先出来。
- 对于 LIFO(后进先出队列),最后进入的元素将首先出来。
- 使用 put(item) 方法将项目添加到队列中。
- 要移除项目,使用 get() 方法。