Python 中的多态性 示例
什么是多态性?
多态性可以定义为一种以多种不同形式出现的状况。它是 Python 编程中的一个概念,其中在 Python 中定义的 对象 可以以不同的方式使用。它允许程序员在派生类中定义多个方法,并且这些方法与父类中的方法同名。这种情况支持 Python 中的方法重载。
运算符中的多态性
Python 中的运算符有助于执行数学和其他各种编程任务。例如,‘+’运算符有助于在 Python 中执行两个整数类型的加法,同样,相同的运算符也有助于在 Python 编程中连接字符串。
让我们以 Python 中的 +(加号)运算符为例,如以下所示,展示多态性在 Python 中的应用:
Python 代码
p = 55
q = 77
r = 9.5
g1 = "Guru"
g2 = "99!"
print("the sum of two numbers",p + q)
print("the data type of result is",type(p + q))
print("The sum of two numbers",q + r)
print("the data type of result is", type (q + r))
print("The concatenated string is", g1 + g2)
print("The data type of two strings",type(g1 + g2))
输出
the sum of two numbers 132 the data type of result is <class 'int'> The sum of the two numbers 86.5 the data type of result is <class 'float'> The concatenated string is Guru99! The data type of two strings <class 'str'>
上面的示例也可以视为运算符重载的示例。
用户定义方法中的多态性
Python 编程语言中的用户定义方法是用户创建的方法,它使用关键字 def 和函数名来声明。
Python 编程语言中的多态性是通过方法重载和方法重写实现的。Python 使用 def 关键字定义方法,并在子类和父类中使用相同的名称。
让我们以上面的示例为例:
Python 代码
from math
import pi
class square:
def __init__(self, length):
self.l = length
def perimeter(self):
return 4 * (self.l)
def area(self):
return self.l * self.l
class Circle:
def __init__(self, radius):
self.r = radius
def perimeter(self):
return 2 * pi * self.r
def area(self):
return pi * self.r * * 2
# Initialize the classes
sqr = square(10)
c1 = Circle(4)
print("Perimeter computed for square: ", sqr.perimeter())
print("Area computed for square: ", sqr.area())
print("Perimeter computed for Circle: ", c1.perimeter())
print("Area computed for Circle: ", c1.area())
输出
Perimeter computed for square: 40 Area computed for square: 100 Perimeter computed for Circle: 25.132741228718345 Area computed for Circle: 50.26548245743669
在上面的代码中,circle 和 square 类中定义了两个用户定义的方法 perimeter 和 area。
如上所示,circle 类和 square 类都调用了相同的方法名,展示了多态性以提供所需输出的特性。
函数中的多态性
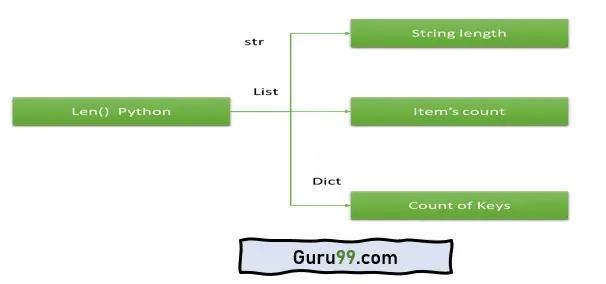
Python 中的内置函数设计得非常兼容,可以执行多种数据类型。在 Python 中,Len() 是一个关键的内置函数。
它适用于多种数据类型:列表、元组、字符串和字典。Len() 函数提供与这些数据类型相关的特定信息。
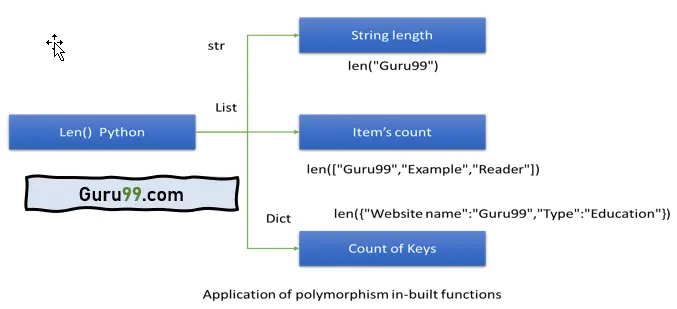
下图显示了多态性如何在 Python 中应用于内置函数:
以下程序有助于说明多态性在 Python 中的应用:
Python 代码
print ("The length of string Guru99 is ",len("Guru99"))
print("The length of list is ",len(["Guru99","Example","Reader"]))
print("The length of dictionary is ",len({"Website name":"Guru99","Type":"Education"}))
输出
The length of string Guru99 is 6 The length of the list is 3 The length of the dictionary is 2
在上面的示例中,Python 的 Len() 函数分别对字符串、列表和字典数据类型执行多态性。
多态性与继承
Python 中的继承可以定义为一种编程概念,其中子类继承了 Python 中存在的另一个基类的属性。
有两个关键的 Python 概念称为方法重写和方法重载。
- 在方法重载中,Python 提供了创建同名方法的功能,以在给定的代码块中执行不同的功能。简单来说,它允许重载方法并使用它们来执行不同的任务。
- 在方法重写中,Python 会覆盖父类和子类中同名的值。
让我们以上面的多态性和继承示例为例:
Python 代码
class baseclass:
def __init__(self, name):
self.name = name
def area1(self):
pass
def __str__(self):
return self.name
class rectangle(baseclass):
def __init__(self, length, breadth):
super().__init__("rectangle")
self.length = length
self.breadth = breadth
def area1(self):
return self.length * self.breadth
class triangle(baseclass):
def __init__(self, height, base):
super().__init__("triangle")
self.height = height
self.base = base
def area1(self):
return (self.base * self.height) / 2
a = rectangle(90, 80)
b = triangle(77, 64)
print("The shape is: ", b)
print("The area of shape is", b.area1())
print("The shape is:", a)
print("The area of shape is", a.area1())
输出
The shape is: a triangle The area of a shape is 2464.0 The shape is: a rectangle The area of a shape is 7200
在上面的代码中,方法具有相同的名称,定义为 init 方法和 area1 方法。然后使用 square 和 rectangle 类的对象调用这两个方法来执行不同的任务,并提供 square 和 rectangle 的面积输出。
类方法的多态性
Python 编程使程序员能够通过类方法实现多态性和方法重载。Python 中的不同类可以拥有在整个 Python 代码中以相同名称声明的方法。
在 Python 中,可以定义两个不同的类。一个将是子类,它从称为父类的另一个已定义类派生属性。
下面的示例说明了类方法的多态性概念:
Python 代码
class amazon:
def __init__(self, name, price):
self.name = name
self.price = price
def info(self):
print("This is product and am class is invoked. The name is {self.name}. This costs {self.price} rupees.")
class flipkart:
def __init__(self, name, price):
self.name = name
self.price = price
def info(self):
print(f "This is product and fli class is invoked. The name is {self.name}. This costs {self.price} rupees.")
FLP = flipkart("Iphone", 2.5)
AMZ = amazon("Iphone", 4)
for product1 in (FLP, AMZ):
product1.info()
输出
This is a product, and fli class is invoked. The name is iPhone, and this costs 2.5 rupees. This is a product, and am class is invoked. The name is iPhone, and this costs 4 rupees.
在上面的代码中,名为 flipkart 和 amazon 的两个不同类使用相同的 info 和 init 方法名称来提供相应产品的价格报价,并进一步说明了 Python 中多态性的概念。
方法重载与编译时多态性之间的区别
在编译时多态性中,Python 程序的编译器会解析调用。编译时多态性通过方法重载来实现。
Python 编译器在运行时不会解析多态性的调用。它也被归类为方法重写,其中相同的方法具有相似的签名或属性,但它们属于不同的类。
摘要
- 多态性可以定义为一种以多种不同形式出现的状况。
- Python 中的运算符有助于执行数学和其他各种编程任务。
- Python 编程语言中的用户定义方法是用户创建的方法,它使用关键字 def 和函数名来声明。
- Python 中的多态性提供了许多理想的特性,例如,它促进了为不同类和方法编写的代码的重用性。
- 子类是派生类,它从父类获取其属性。
- 多态性也通过运行时方法重写和编译时方法重载来实现。
- Python 中的多态性也通过运算符重载和类方法来实现。