PyTest 教程:是什么、如何安装、框架、断言
什么是 PyTest?
PyTest 是一个测试框架,允许用户使用 Python 编程语言编写测试代码。它能帮助您为数据库、API 或 UI 编写简单且可扩展的测试用例。PyTest 主要用于编写 API 测试,它可以帮助编写从简单的单元测试到复杂的函数式测试。
为什么使用 PyTest?
pytest 的一些优点包括:
- 由于其简单易学的语法,上手非常容易。
- 可以并行运行测试。
- 可以运行特定测试或一组测试
- 自动检测测试
- 跳过测试
- 开源
如何安装 PyTest
以下是安装 PyTest 的过程:
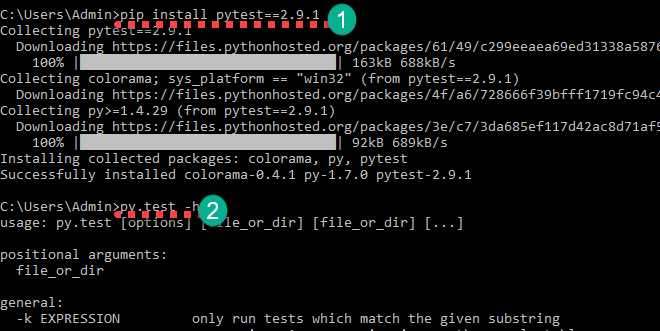
步骤 1) 您可以通过以下方式安装 pytest:
pip install pytest==2.9.1
安装完成后,您可以通过以下方式进行确认:
py.test -h
这将显示帮助信息
第一个基础 PyTest
现在,我们将学习如何使用 Pytest 和一个基础的 PyTest 示例。
创建一个名为 study_pytest 的文件夹。我们将在该文件夹内创建测试文件。
请在命令行中导航到该文件夹。
在文件夹内创建一个名为 test_sample1.py 的文件
在其中添加以下代码并保存
import pytest def test_file1_method1(): x=5 y=6 assert x+1 == y,"test failed" assert x == y,"test failed" def test_file1_method2(): x=5 y=6 assert x+1 == y,"test failed"
使用以下命令运行测试:
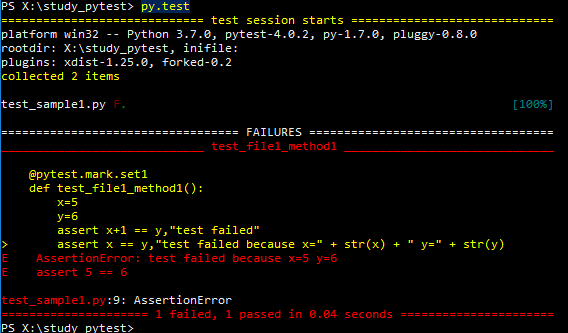
py.test
您将收到如下输出:
test_sample1.py F.
============================================== FAILURES ========================================
____________________________________________ test_sample1 ______________________________________
def test_file1_method1():
x=5
y=6
assert x+1 == y,"test failed"
> assert x == y,"test failed"
E AssertionError: test failed
E assert 5 == 6
test_sample1.py:6: AssertionError
在 test_sample1.py 文件中,F 表示失败。
F 表示失败
点 (.) 表示成功。
在失败部分,您可以查看失败的方法和失败的行。这里的 x==y 表示 5==6,这是错误的。
接下来,在本 PyTest 教程中,我们将学习 PyTest 中的断言。
PyTest 中的断言
Pytest 断言是返回 True 或 False 状态的检查。在 Python Pytest 中,如果测试方法中的断言失败,则该方法的执行将在那里停止。该测试方法中剩余的代码不会被执行,而 Pytest 断言将继续执行下一个测试方法。
Pytest 断言示例
assert "hello" == "Hai" is an assertion failure. assert 4==4 is a successful assertion assert True is a successful assertion assert False is an assertion failure.
考虑一下:
assert x == y,"test failed because x=" + str(x) + " y=" + str(y)
将此代码放在 test_file1_method1() 中,而不是断言。
assert x == y,"test failed"
运行测试将导致 AssertionError: test failed x=5 y=6 错误。
PyTest 如何识别测试文件和测试方法
默认情况下,pytest 仅将以 test_ 开头或以 _test 结尾的文件名识别为测试文件。我们可以显式提及其他文件名(稍后会解释)。Pytest 要求测试方法名以 “test” 开头。所有其他方法名都将被忽略,即使我们显式要求运行这些方法。
请看一些有效的和无效的 pytest 文件名示例。
test_login.py - valid login_test.py - valid testlogin.py -invalid logintest.py -invalid
注意:是的,我们可以显式要求 pytest 选择 testlogin.py 和 logintest.py。
请看一些有效的和无效的 pytest 测试方法示例。
def test_file1_method1(): - valid def testfile1_method1(): - valid def file1_method1(): - invalid
注意:即使我们显式提及 file1_method1(),pytest 也不会运行此方法。
从特定文件和多个文件中运行多个测试
当前,在 study_pytest 文件夹内,我们有一个文件 test_sample1.py。假设我们有多个文件,例如 test_sample2.py,test_sample3.py。要运行文件夹和子文件夹中所有文件中的所有测试,我们只需运行 pytest 命令。
py.test
这将运行该文件夹及该文件夹下的子文件夹中所有以 test_ 开头和以 _test 结尾的文件名。
要仅从特定文件运行测试,我们可以使用 py.test <文件名>
py.test test_sample1.py
使用 PyTest 运行整个测试的子集
有时我们不想运行整个测试套件。Pytest 允许我们运行特定的测试。我们可以通过 2 种方式实现:
- 通过子字符串匹配对测试名称进行分组
- 通过标记对测试进行分组
我们已经有了 test_sample1.py。创建一个文件 test_sample2.py 并将以下代码添加到其中。
def test_file2_method1(): x=5 y=6 assert x+1 == y,"test failed" assert x == y,"test failed because x=" + str(x) + " y=" + str(y) def test_file2_method2(): x=5 y=6 assert x+1 == y,"test failed"
所以我们目前拥有:
• test_sample1.py • test_file1_method1() • test_file1_method2() • test_sample2.py • test_file2_method1() • test_file2_method2()
选项 1) 通过子字符串匹配运行测试
在这里,要运行名称中包含 method1 的所有测试,我们必须运行:
py.test -k method1 -v -k <expression> is used to represent the substring to match -v increases the verbosity
因此,运行 py.test -k method1 -v 将得到以下结果:
test_sample2.py::test_file2_method1 FAILED
test_sample1.py::test_file1_method1 FAILED
============================================== FAILURES ==============================================
_________________________________________ test_file2_method1 _________________________________________
def test_file2_method1():
x=5
y=6
assert x+1 == y,"test failed"
> assert x == y,"test failed because x=" + str(x) + " y=" + str(y)
E AssertionError: test failed because x=5 y=6
E assert 5 == 6
test_sample2.py:5: AssertionError
_________________________________________ test_file1_method1 _________________________________________
@pytest.mark.only
def test_file1_method1():
x=5
y=6
assert x+1 == y,"test failed"
> assert x == y,"test failed because x=" + str(x) + " y=" + str(y)
E AssertionError: test failed because x=5 y=6
E assert 5 == 6
test_sample1.py:8: AssertionError
================================= 2 tests deselected by '-kmethod1' ==================================
=============================== 2 failed, 2 deselected in 0.02 seconds ===============================
在这里,您可以看到结尾处有 2 个测试被 ‘-kmethod1’ 跳过,它们是 test_file1_method2 和 test_file2_method2。
尝试使用各种组合运行,例如:
py.test -k method -v - will run all the four methods py.test -k methods -v – will not run any test as there is no test name matches the substring 'methods'
选项 2) 通过标记运行测试
Pytest 允许我们使用 pytest 标记 @pytest.mark 来为测试方法设置各种属性。要在测试文件中使用标记,我们需要在测试文件中导入 pytest。
这里我们将为测试方法应用不同的标记名称,并根据标记名称运行特定的测试。我们可以通过使用以下方式在每个测试名称上定义标记:
@pytest.mark.<name>.
我们正在为测试方法定义 set1 和 set2 标记,并将使用标记名称运行测试。使用以下代码更新测试文件:
test_sample1.py
import pytest @pytest.mark.set1 def test_file1_method1(): x=5 y=6 assert x+1 == y,"test failed" assert x == y,"test failed because x=" + str(x) + " y=" + str(y) @pytest.mark.set2 def test_file1_method2(): x=5 y=6 assert x+1 == y,"test failed"
test_sample2.py
import pytest @pytest.mark.set1 def test_file2_method1(): x=5 y=6 assert x+1 == y,"test failed" assert x == y,"test failed because x=" + str(x) + " y=" + str(y) @pytest.mark.set1 def test_file2_method2(): x=5 y=6 assert x+1 == y,"test failed"
我们可以通过以下方式运行标记的测试:
py.test -m <name> -m <name> mentions the marker name
运行 py.test -m set1。这将运行 test_file1_method1、test_file2_method1、test_file2_method2 方法。
运行 py.test -m set2 将运行 test_file1_method2。
使用 Pytest 并行运行测试
通常,一个测试套件将包含多个测试文件和数百个测试方法,这需要相当长的时间来执行。Pytest 允许我们并行运行测试。
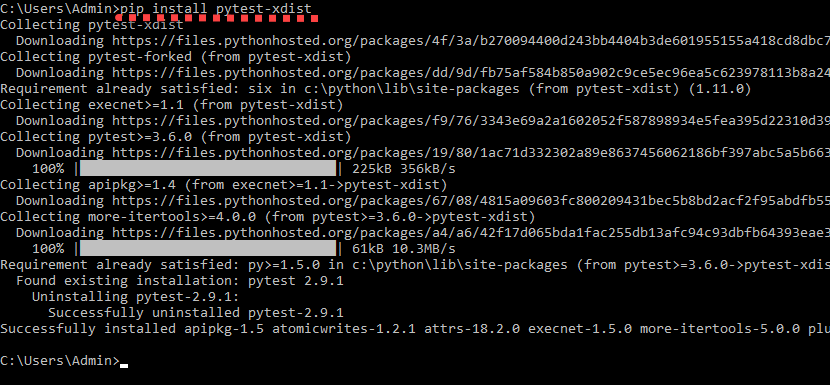
为此,我们首先需要通过运行以下命令安装 pytest-xdist:
pip install pytest-xdist
您现在可以通过以下方式运行测试:
py.test -n 4
-n <num> 使用多个工作进程运行测试。在上面的命令中,将有 4 个工作进程来运行测试。
Pytest Fixtures
Fixtures (夹具) 用于在我们想在每个测试方法之前运行一些代码时。因此,而不是在每个测试中重复相同的代码,我们定义了 fixtures。通常,fixtures 用于初始化数据库连接、传递基础 URL 等。
一个方法通过使用以下标记来标记为 Pytest fixture:
@pytest.fixture
测试方法可以通过将 fixture 作为输入参数来使用 Pytest fixture。
使用以下代码创建一个新文件 test_basic_fixture.py:
import pytest @pytest.fixture def supply_AA_BB_CC(): aa=25 bb =35 cc=45 return [aa,bb,cc] def test_comparewithAA(supply_AA_BB_CC): zz=35 assert supply_AA_BB_CC[0]==zz,"aa and zz comparison failed" def test_comparewithBB(supply_AA_BB_CC): zz=35 assert supply_AA_BB_CC[1]==zz,"bb and zz comparison failed" def test_comparewithCC(supply_AA_BB_CC): zz=35 assert supply_AA_BB_CC[2]==zz,"cc and zz comparison failed"
这里
- 我们有一个名为 supply_AA_BB_CC 的 fixture。此方法将返回一个包含 3 个值的列表。
- 我们有 3 个测试方法,分别与其中一个值进行比较。
每个测试函数都有一个输入参数,其名称与可用的 fixture 匹配。Pytest 然后调用相应的 fixture 方法,并将返回的值存储在输入参数中,这里是列表 [25,35,45]。现在,测试方法正在使用列表项进行比较。
现在运行测试并查看结果:
py.test test_basic_fixture
test_basic_fixture.py::test_comparewithAA FAILED
test_basic_fixture.py::test_comparewithBB PASSED
test_basic_fixture.py::test_comparewithCC FAILED
============================================== FAILURES ==============================================
_________________________________________ test_comparewithAA _________________________________________
supply_AA_BB_CC = [25, 35, 45]
def test_comparewithAA(supply_AA_BB_CC):
zz=35
> assert supply_AA_BB_CC[0]==zz,"aa and zz comparison failed"
E AssertionError: aa and zz comparison failed
E assert 25 == 35
test_basic_fixture.py:10: AssertionError
_________________________________________ test_comparewithCC _________________________________________
supply_AA_BB_CC = [25, 35, 45]
def test_comparewithCC(supply_AA_BB_CC):
zz=35
> assert supply_AA_BB_CC[2]==zz,"cc and zz comparison failed"
E AssertionError: cc and zz comparison failed
E assert 45 == 35
test_basic_fixture.py:16: AssertionError
================================= 2 failed, 1 passed in 0.05 seconds =================================
测试 test_comparewithBB 通过,因为 zz=BB=35,而其余 2 个测试失败。
fixture 方法的作用域仅限于其定义的测试文件。如果我们尝试在其他测试文件中访问 fixture,我们将收到一个错误,提示 fixture 'supply_AA_BB_CC' 未找到,用于其他文件中的测试方法。
要使用相同的 fixture 跨多个测试文件,我们将创建一个名为 conftest.py 的文件来定义 fixture 方法。
让我们通过以下 PyTest 示例来看一下。创建 3 个文件 conftest.py、test_basic_fixture.py、test_basic_fixture2.py,其中包含以下代码:
conftest.py
import pytest @pytest.fixture def supply_AA_BB_CC(): aa=25 bb =35 cc=45 return [aa,bb,cc]
test_basic_fixture.py
import pytest def test_comparewithAA(supply_AA_BB_CC): zz=35 assert supply_AA_BB_CC[0]==zz,"aa and zz comparison failed" def test_comparewithBB(supply_AA_BB_CC): zz=35 assert supply_AA_BB_CC[1]==zz,"bb and zz comparison failed" def test_comparewithCC(supply_AA_BB_CC): zz=35 assert supply_AA_BB_CC[2]==zz,"cc and zz comparison failed"
test_basic_fixture2.py
import pytest def test_comparewithAA_file2(supply_AA_BB_CC): zz=25 assert supply_AA_BB_CC[0]==zz,"aa and zz comparison failed" def test_comparewithBB_file2(supply_AA_BB_CC): zz=25 assert supply_AA_BB_CC[1]==zz,"bb and zz comparison failed" def test_comparewithCC_file2(supply_AA_BB_CC): zz=25 assert supply_AA_BB_CC[2]==zz,"cc and zz comparison failed"
pytest 会首先在测试文件中查找 fixture,如果找不到,它会在 conftest.py 中查找。
通过 py.test -k test_comparewith -v 运行测试以获得如下结果:
test_basic_fixture.py::test_comparewithAA FAILED test_basic_fixture.py::test_comparewithBB PASSED test_basic_fixture.py::test_comparewithCC FAILED test_basic_fixture2.py::test_comparewithAA_file2 PASSED test_basic_fixture2.py::test_comparewithBB_file2 FAILED test_basic_fixture2.py::test_comparewithCC_file2 FAILED
Pytest 参数化测试
参数化测试的目的是针对多组参数运行测试。我们可以通过 @pytest.mark.parametrize 来实现。
我们将通过以下 PyTest 示例来演示。在这里,我们将向测试方法传递 3 个参数。此测试方法将相加前 2 个参数,并与第 3 个参数进行比较。
使用以下代码创建测试文件 test_addition.py:
import pytest
@pytest.mark.parametrize("input1, input2, output",[(5,5,10),(3,5,12)])
def test_add(input1, input2, output):
assert input1+input2 == output,"failed"
这里,测试方法接受 3 个参数:input1、input2、output。它将 input1 和 input2 相加,并与 output 进行比较。
让我们通过 py.test -k test_add -v 运行测试并查看结果:
test_addition.py::test_add[5-5-10] PASSED
test_addition.py::test_add[3-5-12] FAILED
============================================== FAILURES ==============================================
__________________________________________ test_add[3-5-12] __________________________________________
input1 = 3, input2 = 5, output = 12
@pytest.mark.parametrize("input1, input2, output",[(5,5,10),(3,5,12)])
def test_add(input1, input2, output):
> assert input1+input2 == output,"failed"
E AssertionError: failed
E assert (3 + 5) == 12
test_addition.py:5: AssertionError
您可以看到测试运行了 2 次 – 一次是检查 5+5 ==10,另一次是检查 3+5 ==12。
test_addition.py::test_add[5-5-10] PASSED (通过)
test_addition.py::test_add[3-5-12] FAILED (失败)
Pytest Xfail / Skip Tests (跳过/标记失败测试)
在某些情况下,我们可能不想执行某个测试,或者某个 测试用例 在特定时间点不相关。在这些情况下,我们可以选择 Xfail 测试或跳过测试。
xfail 测试将被执行,但不会被计入失败或成功的测试中。如果该测试失败,将不会显示回溯。我们可以使用以下方式 xfail 测试:
@pytest.mark.xfail。
跳过测试意味着该测试将不会被执行。我们可以使用以下方式跳过测试:
@pytest.mark.skip。
使用以下代码编辑 test_addition.py:
import pytest @pytest.mark.skip def test_add_1(): assert 100+200 == 400,"failed" @pytest.mark.skip def test_add_2(): assert 100+200 == 300,"failed" @pytest.mark.xfail def test_add_3(): assert 15+13 == 28,"failed" @pytest.mark.xfail def test_add_4(): assert 15+13 == 100,"failed" def test_add_5(): assert 3+2 == 5,"failed" def test_add_6(): assert 3+2 == 6,"failed"
这里
- test_add_1 和 test_add_2 被跳过,不会执行。
- test_add_3 和 test_add_4 被标记为 xfailed。这些测试将被执行,并将计入 xfailed(在测试失败时)或 xpassed(在测试成功时)测试中。失败时不会有任何回溯。
- test_add_5 和 test_add_6 将被执行,test_add_6 将报告带有回溯的失败,而 test_add_5 则通过。
通过 py.test test_addition.py -v 执行测试并查看结果:
test_addition.py::test_add_1 SKIPPED
test_addition.py::test_add_2 SKIPPED
test_addition.py::test_add_3 XPASS
test_addition.py::test_add_4 xfail
test_addition.py::test_add_5 PASSED
test_addition.py::test_add_6 FAILED
============================================== FAILURES ==============================================
_____________________________________________ test_add_6 _____________________________________________
def test_add_6():
> assert 3+2 == 6,"failed"
E AssertionError: failed
E assert (3 + 2) == 6
test_addition.py:24: AssertionError
================ 1 failed, 1 passed, 2 skipped, 1 xfailed, 1 xpassed in 0.07 seconds =================
Results XML (结果 XML)
我们可以创建 XML 格式的测试结果,并将其提供给持续集成服务器进行进一步处理等。这可以通过以下方式完成:
py.test test_sample1.py -v –junitxml=”result.xml”
result.xml 将记录测试执行结果。下面是一个示例 result.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<testsuite errors="0" failures="1" name="pytest" skips="0" tests="2" time="0.046">
<testcase classname="test_sample1" file="test_sample1.py" line="3" name="test_file1_method1" time="0.001384973526">
<failure message="AssertionError:test failed because x=5 y=6 assert 5 ==6">
@pytest.mark.set1
def test_file1_method1():
x=5
y=6
assert x+1 == y,"test failed"
> assert x == y,"test failed because x=" + str(x) + " y=" + str(y)
E AssertionError: test failed because x=5 y=6
E assert 5 == 6
test_sample1.py:9: AssertionError
</failure>
</testcase>
<testcase classname="test_sample1" file="test_sample1.py" line="10" name="test_file1_method2" time="0.000830173492432" />
</testsuite>
从 <testsuite errors=”0″ failures=”1″ name=”pytest” skips=”0″ tests=”2″ time=”0.046″> 中,我们可以看到总共有两个测试,其中一个失败了。在此下方,您可以在 <testcase> 标签下看到关于每个已执行测试的详细信息。
Pytest 框架测试 API
现在我们将创建一个小型 pytest 框架来测试 API。这里使用的 API 是来自 https://reqres.in/ 的免费 API。该网站仅用于提供可测试的 API。该网站不会存储我们的数据。
在这里,我们将编写一些测试来:
- 列出用户
- 用户登录
创建以下文件并包含给定代码:
conftest.py – 包含一个 fixture,该 fixture 将为所有测试方法提供基本 URL
import pytest @pytest.fixture def supply_url(): return "https://reqres.in/api"
test_list_user.py – 包含列出有效和无效用户的测试方法
- test_list_valid_user 测试有效的用户获取并验证响应
- test_list_invaliduser 测试无效的用户获取并验证响应
import pytest
import requests
import json
@pytest.mark.parametrize("userid, firstname",[(1,"George"),(2,"Janet")])
def test_list_valid_user(supply_url,userid,firstname):
url = supply_url + "/users/" + str(userid)
resp = requests.get(url)
j = json.loads(resp.text)
assert resp.status_code == 200, resp.text
assert j['data']['id'] == userid, resp.text
assert j['data']['first_name'] == firstname, resp.text
def test_list_invaliduser(supply_url):
url = supply_url + "/users/50"
resp = requests.get(url)
assert resp.status_code == 404, resp.text
test_login_user.py – 包含用于测试登录功能的测试方法。
- test_login_valid 使用电子邮件和密码测试有效的登录尝试
- test_login_no_password 测试不传递密码的无效登录尝试
- test_login_no_email 测试不传递电子邮件的无效登录尝试。
import pytest
import requests
import json
def test_login_valid(supply_url):
url = supply_url + "/login/"
data = {'email':'test@test.com','password':'something'}
resp = requests.post(url, data=data)
j = json.loads(resp.text)
assert resp.status_code == 200, resp.text
assert j['token'] == "QpwL5tke4Pnpja7X", resp.text
def test_login_no_password(supply_url):
url = supply_url + "/login/"
data = {'email':'test@test.com'}
resp = requests.post(url, data=data)
j = json.loads(resp.text)
assert resp.status_code == 400, resp.text
assert j['error'] == "Missing password", resp.text
def test_login_no_email(supply_url):
url = supply_url + "/login/"
data = {}
resp = requests.post(url, data=data)
j = json.loads(resp.text)
assert resp.status_code == 400, resp.text
assert j['error'] == "Missing email or username", resp.text
使用 py.test -v 运行测试
查看结果如下:
test_list_user.py::test_list_valid_user[1-George] PASSED test_list_user.py::test_list_valid_user[2-Janet] PASSED test_list_user.py::test_list_invaliduser PASSED test_login_user.py::test_login_valid PASSED test_login_user.py::test_login_no_password PASSED test_login_user.py::test_login_no_email PASSED
更新测试并尝试各种输出
摘要
在本 PyTest 教程中,我们涵盖了:
- 使用 pip install pytest=2.9.1 安装 pytest
- 简单的 pytest 程序并使用 py.test 命令运行它。
- 断言语句,assert x==y,将返回 True 或 False。
- Pytest 如何识别测试文件和方法。
- 以 test_ 开头或以 _test 结尾的测试文件
- 以 test 开头的测试方法
- py.test 命令将运行该文件夹及子文件夹中的所有测试文件。要运行特定文件,我们可以使用命令 py.test <文件名>
- 运行测试子集
- 通过子字符串匹配对测试名称进行分组。py.test -k <名称> -v 将运行名称中包含 <名称> 的所有测试。
- 通过标记运行测试。使用 @pytest.mark.<name> 标记测试,并使用 pytest -m <name> 运行标记为 <name> 的测试。
- 并行运行测试
- 使用 pip install pytest-xdist 安装 pytest-xdist
- 使用 py.test -n NUM 运行测试,其中 NUM 是工作进程的数量
- 创建 fixture 方法以通过使用 @pytest.fixture 标记方法在每个测试之前运行代码
- fixture 方法的作用域仅限于其定义的测试文件。
- 通过在 conftest.py 文件中定义 fixture 方法,可以跨多个测试文件访问该 fixture 方法。
- 测试方法可以通过将其用作输入参数来访问 Pytest fixture。
- 参数化测试以针对多组输入运行它。
@pytest.mark.parametrize(“input1, input2, output”,[(5,5,10),(3,5,12)])
def test_add(input1, input2, output)
assert input1+input2 == output,”failed”
将使用输入 (5,5,10) 和 (3,5,12) 运行测试。 - 使用 @pytets.mark.skip 和 @pytest.mark.xfail 跳过/标记为 xfail 的测试
- 使用 py.test test_sample1.py -v –junitxml=”result.xml” 创建 XML 格式的测试结果,其中包含已执行的测试详情。
- 一个示例 pytest 框架,用于测试 API