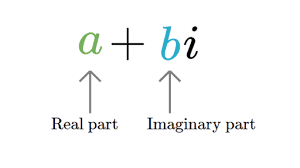Python JSON:编码 (dumps)、解码 (loads) 和 读取 JSON 文件
Python 中的 JSON 是什么?
Python 中的 JSON 是一种标准的、受 JavaScript 启发的格式,用于数据交换和作为文本格式在网络上传输数据。通常,JSON 是字符串或文本格式。它可以被 API 和数据库使用,并以键/值对的形式表示对象。JSON 的意思是 JavaScript 对象表示法(JavaScript Object Notation)。
Python JSON 语法
JSON 以键值对的形式编写。
{
"Key": "Value",
"Key": "Value",
}
JSON 非常类似于 Python 字典。 Python 支持 JSON,并且拥有一个内置的 JSON 库。
Python 中的 JSON 库
Python 的‘marshal’和‘pickle’外部模块维护着一个 JSON Python 库的版本。要在 Python 中使用 JSON 来执行 JSON 相关操作,如编码和解码,您需要先导入 JSON 库,为此,在您的 .py 文件中,
import json
JSON Python 模块提供以下方法
| 方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| dumps() | 编码为 JSON 对象 |
| dump() | 将编码后的字符串写入文件 |
| loads() | 解码 JSON 字符串 |
| load() | 读取 JSON 文件时进行解码 |
Python 到 JSON(编码)
JSON Python 库默认执行以下 Python 对象到 JSON 对象的转换
| Python | JSON |
|---|---|
| dict | 对象 |
| list | 数组 |
| unicode | 字符串 |
| number – int, long | number – int |
| float | number – real |
| 真 | 真 |
| 假 | 假 |
| 无 | Null |
将 Python 数据转换为 JSON 称为编码操作。编码是通过 JSON 库方法 – dumps() 完成的。
Python 中的 JSON dumps()
Python 中的json.dumps()是一种将 Python 的字典对象转换为 JSON 字符串数据格式的方法。当需要将对象以字符串格式用于解析、打印等操作时,它非常有用。
现在让我们通过 Python 执行第一个 json.dumps 编码示例
import json
x = {
"name": "Ken",
"age": 45,
"married": True,
"children": ("Alice","Bob"),
"pets": ['Dog'],
"cars": [
{"model": "Audi A1", "mpg": 15.1},
{"model": "Zeep Compass", "mpg": 18.1}
]
}
# sorting result in asscending order by keys:
sorted_string = json.dumps(x, indent=4, sort_keys=True)
print(sorted_string)
输出
{"person": {"name": "Kenn", "sex": "male", "age": 28}})
让我们通过使用相同的函数 dump() 来看一下 Python 写入 JSON 到文件的示例,以创建字典的 JSON 文件。
# here we create new data_file.json file with write mode using file i/o operation
with open('json_file.json', "w") as file_write:
# write json data into file
json.dump(person_data, file_write)
输出
没有显示什么……您的系统中已创建 json_file.json 文件。您可以在下面的写入 JSON 到文件 Python 示例中检查该文件。
JSON 到 Python(解码)
JSON 字符串解码是通过 Python JSON 库的内置方法 json.loads() 和 json.load() 完成的。这里的转换表显示了 JSON 对象到 Python 对象 的示例,这有助于在 Python 中执行 JSON 字符串的解码。
| JSON | Python |
|---|---|
| 对象 | dict |
| 数组 | list |
| 字符串 | unicode |
| number – int | number – int, long |
| number – real | float |
| 真 | 真 |
| 假 | 假 |
| Null | 无 |
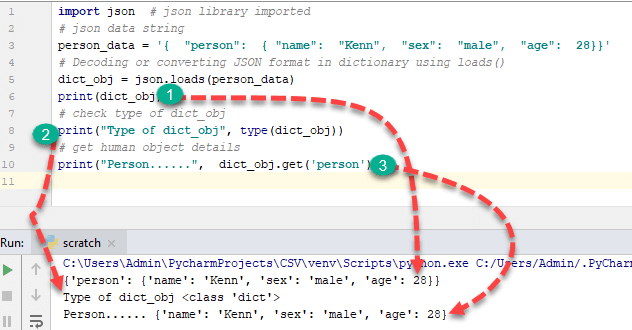
让我们通过 json.loads 函数来看一个基本的解析 JSON Python 解码示例。
import json # json library imported
# json data string
person_data = '{ "person": { "name": "Kenn", "sex": "male", "age": 28}}'
# Decoding or converting JSON format in dictionary using loads()
dict_obj = json.loads(person_data)
print(dict_obj)
# check type of dict_obj
print("Type of dict_obj", type(dict_obj))
# get human object details
print("Person......", dict_obj.get('person'))
输出
{'person': {'name': 'Kenn', 'sex': 'male', 'age': 28}}
Type of dict_obj <class 'dict'>
Person...... {'name': 'John', 'sex': 'male'}
解码 JSON 文件或解析 Python 中的 JSON 文件
现在,我们将学习如何在 Python 中读取 JSON 文件,并附带 Python 解析 JSON 示例。
注意:解码 JSON 文件是与文件输入/输出 (I/O) 相关的操作。JSON 文件必须存在于您的系统中,位于您在程序中指定的目录。
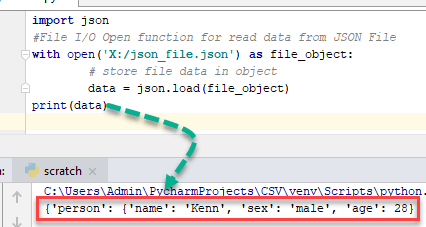
Python 读取 JSON 文件示例
import json
#File I/O Open function for read data from JSON File
with open('X:/json_file.json') as file_object:
# store file data in object
data = json.load(file_object)
print(data)
在上方的 Python 读取 JSON 文件示例中所示,here data 是一个 Python 字典对象。
输出
{'person': {'name': 'Kenn', 'sex': 'male', 'age': 28}}
Python 中的紧凑编码
当您需要减小 JSON 文件大小时,可以在 Python 中使用紧凑编码。
示例,
import json
# Create a List that contains dictionary
lst = ['a', 'b', 'c',{'4': 5, '6': 7}]
# separator used for compact representation of JSON.
# Use of ',' to identify list items
# Use of ':' to identify key and value in dictionary
compact_obj = json.dumps(lst, separators=(',', ':'))
print(compact_obj)
输出
'["a", "b", "c", {"4": 5, "6": 7}]'
** Here output of JSON is represented in a single line which is the most compact representation by removing the space character from compact_obj **
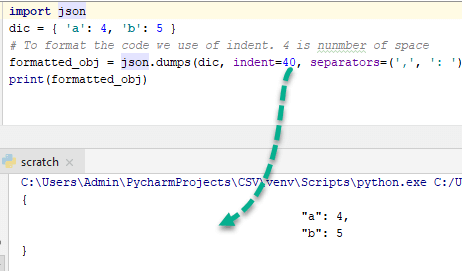
格式化 JSON 代码(美化打印)
- 目的是编写人类可读的优质代码。借助美化打印,任何人都可以轻松理解代码。
示例
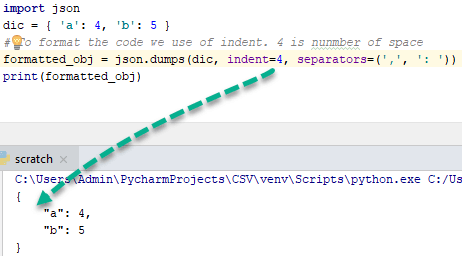
import json
dic = { 'a': 4, 'b': 5 }
''' To format the code use of indent and 4 shows number of space and use of separator is not necessary but standard way to write code of particular function. '''
formatted_obj = json.dumps(dic, indent=4, separators=(',', ': '))
print(formatted_obj)
输出
{
"a" : 4,
"b" : 5
}
为了更好地理解这一点,请将 indent 改为 40 并观察输出-
排序 JSON 代码
Python dumps 函数参数中的 sort_keys 属性将按字母顺序对 JSON 中的键进行排序。sort_keys 属性是一个布尔属性。当它为 true 时允许排序,否则不允许。让我们通过 Python 字符串到 JSON 排序示例来理解。
示例,
import json
x = {
"name": "Ken",
"age": 45,
"married": True,
"children": ("Alice", "Bob"),
"pets": [ 'Dog' ],
"cars": [
{"model": "Audi A1", "mpg": 15.1},
{"model": "Zeep Compass", "mpg": 18.1}
],
}
# sorting result in asscending order by keys:
sorted_string = json.dumps(x, indent=4, sort_keys=True)
print(sorted_string)
输出
{
"age": 45,
"cars": [ {
"model": "Audi A1",
"mpg": 15.1
},
{
"model": "Zeep Compass",
"mpg": 18.1
}
],
"children": [ "Alice",
"Bob"
],
"married": true,
"name": "Ken",
"pets": [
"Dog"
]
}
正如您可能注意到的,键 age、cars、children 等已按字母顺序排列。
Python 的复杂对象编码
复杂对象由两个不同的部分组成:
- 实部
- 虚部
示例:3 + 2i
在对复杂对象进行编码之前,您需要检查一个变量是否为复杂类型。您需要创建一个函数,该函数使用实例方法来检查存储在变量中的值。
让我们创建特定函数来检查对象是否为复杂类型或是否符合编码要求。
import json
# create function to check instance is complex or not
def complex_encode(object):
# check using isinstance method
if isinstance(object, complex):
return [object.real, object.imag]
# raised error using exception handling if object is not complex
raise TypeError(repr(object) + " is not JSON serialized")
# perform json encoding by passing parameter
complex_obj = json.dumps(4 + 5j, default=complex_encode)
print(complex_obj)
输出
'[4.0, 5.0]'
Python 中的复杂 JSON 对象解码
要解码 JSON 中的复杂对象,请使用 object_hook 参数,该参数会检查 JSON 字符串是否包含复杂对象。让我们通过 Python 字符串到 JSON 示例来理解。
import json
# function check JSON string contains complex object
def is_complex(objct):
if '__complex__' in objct:
return complex(objct['real'], objct['img'])
return objct
# use of json loads method with object_hook for check object complex or not
complex_object =json.loads('{"__complex__": true, "real": 4, "img": 5}', object_hook = is_complex)
#here we not passed complex object so it's convert into dictionary
simple_object =json.loads('{"real": 6, "img": 7}', object_hook = is_complex)
print("Complex_object......",complex_object)
print("Without_complex_object......",simple_object)
输出
Complex_object...... (4+5j)
Without_complex_object...... {'real': 6, 'img': 7}
JSON 序列化类 JSONEncoder 概述
JSONEncoder 类用于在编码时序列化任何 Python 对象。它包含三个不同的编码方法,分别是:
- default(o) – 在子类中实现,并为 o 对象返回可序列化的对象。
- encode(o) – 与 JSON dumps Python 方法相同,返回 Python 数据结构的 JSON 字符串。
- iterencode(o) – 一次表示一个字符串并编码对象 o。
借助 JSONEncoder 类的 encode() 方法,我们还可以像下面的 Python JSON 编码示例一样编码任何 Python 对象。
# import JSONEncoder class from json
from json.encoder import JSONEncoder
colour_dict = { "colour": ["red", "yellow", "green" ]}
# directly called encode method of JSON
JSONEncoder().encode(colour_dict)
输出
'{"colour": ["red", "yellow", "green"]}'
JSON 反序列化类 JSONDecoder 概述
JSONDecoder 类用于在解码时反序列化任何 Python 对象。它包含三个不同的解码方法,分别是:
- default(o) – 在子类中实现,并返回反序列化的对象 o。
- decode(o) – 与 json.loads() 方法相同,返回 JSON 字符串或数据的 Python 数据结构。
- raw_decode(o) – 一次表示一个 Python 字典并解码对象 o。
借助 JSONDecoder 类的 decode() 方法,我们还可以像下面的 Python JSON 解码示例一样解码 JSON 字符串。
import json
# import JSONDecoder class from json
from json.decoder import JSONDecoder
colour_string = '{ "colour": ["red", "yellow"]}'
# directly called decode method of JSON
JSONDecoder().decode(colour_string)
输出
{'colour': ['red', 'yellow']}
从 URL 解码 JSON 数据:实际示例
我们将从指定 URL(https://gbfs.citibikenyc.com/gbfs/2.3/gbfs.json)获取 CityBike NYC(自行车共享系统)的数据,并将其转换为字典格式。
Python 从文件加载 JSON 示例
注意:- 确保您的 Python 中已安装 requests 库。如果没有,请打开终端或 CMD 并输入:
- (Python 3 或更高版本)pip3 install requests
import json
import requests
# get JSON string data from CityBike NYC using web requests library
json_response= requests.get("https://gbfs.citibikenyc.com/gbfs/2.3/gbfs.json")
# check type of json_response object
print(type(json_response.text))
# load data in loads() function of json library
bike_dict = json.loads(json_response.text)
#check type of news_dict
print(type(bike_dict))
# now get stationBeanList key data from dict
print(bike_dict['stationBeanList'][0])
输出
<class 'str'>
<class 'dict'>
{
'id': 487,
'stationName': 'E 20 St & FDR Drive',
'availableDocks': 24,
'totalDocks': 34,
'latitude': 40.73314259,
'longitude': -73.97573881,
'statusValue': 'In Service',
'statusKey': 1,
'availableBikes': 9,
'stAddress1': 'E 20 St & FDR Drive',
'stAddress2': '',
'city': '',
'postalCode': '',
'location': '',
'altitude': '',
'testStation': False,
'lastCommunicationTime': '2018-12-11 10:59:09 PM', 'landMark': ''
}
Python JSON 库相关的异常
- 类 json.JSONDecoderError 处理与解码操作相关的异常。它是 ValueError 的子类。
- 异常 – json.JSONDecoderError(msg, doc)
- 异常的参数包括:
- msg – 未格式化的错误消息
- doc – 解析的 JSON 文档
- pos – 文档失败时的起始索引
- lineno – 行号,对应于 pos
- colon – 列号,对应于 pos
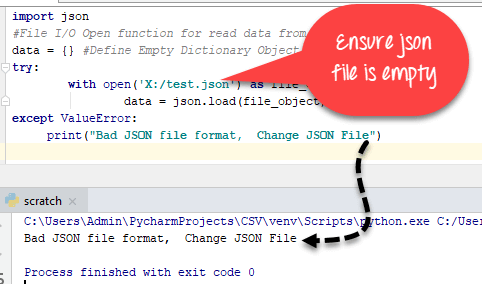
Python 从文件加载 JSON 示例
import json
#File I/O Open function for read data from JSON File
data = {} #Define Empty Dictionary Object
try:
with open('json_file_name.json') as file_object:
data = json.load(file_object)
except ValueError:
print("Bad JSON file format, Change JSON File")
Python 中的无穷大和 NaN 数字
JSON 数据交换格式(RFC – Request For Comments)不允许无穷大或 Nan 值,但在 Python-JSON 库中执行无穷大和 Nan 值相关的操作没有限制。如果 JSON 包含 INFINITE 和 Nan 数据类型,它会将其转换为字面量。
示例,
import json
# pass float Infinite value
infinite_json = json.dumps(float('inf'))
# check infinite json type
print(infinite_json)
print(type(infinite_json))
json_nan = json.dumps(float('nan'))
print(json_nan)
# pass json_string as Infinity
infinite = json.loads('Infinity')
print(infinite)
# check type of Infinity
print(type(infinite))
输出
Infinity <class 'str'> NaN inf <class 'float'>
JSON 字符串中的重复键
RFC 规定 JSON 对象中的键名应该是唯一的,但这不是强制性的。Python JSON 库不会引发重复对象在 JSON 中的异常。它会忽略所有重复的键值对,只考虑最后一个键值对。
- 示例,
import json
repeat_pair = '{"a": 1, "a": 2, "a": 3}'
json.loads(repeat_pair)
输出
{'a': 3}
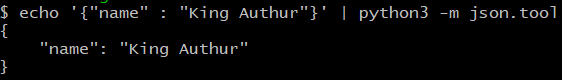
Python 中带 JSON 的 CLI(命令行界面)
json.tool 提供了一个命令行界面来验证 JSON 的美化打印语法。让我们看一个 CLI 示例。
$ echo '{"name" : "Kings Authur" }' | python3 -m json.tool
输出
{
"name": " Kings Authur "
}
Python 中 JSON 的优点
- 在容器和值之间轻松切换(JSON 到 Python 和 Python 到 JSON)
- 人类可读(美化打印)JSON 对象
- 在数据处理中广泛使用。
- 单个文件中没有相同的数据结构。
Python 中 JSON 的实现限制
- 在 JSON 的反序列化器中,数字的范围和预测。
- JSON 字符串的最大长度、JSON 数组以及对象的嵌套级别。
Python JSON 速查表
| Python JSON 函数 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| json.dumps(person_data) | 创建 JSON 对象 |
| json.dump(person_data, file_write) | 使用 Python 的文件 I/O 创建 JSON 文件 |
| compact_obj = json.dumps(data, separators=(‘,’,’:’)) | 通过使用 separator 从 JSON 对象中移除空格字符来创建紧凑的 JSON 对象。 |
| formatted_obj = json.dumps(dic, indent=4, separators=(‘,’, ‘: ‘)) | 使用 Indent 格式化 JSON 代码 |
| sorted_string = json.dumps(x, indent=4, sort_keys=True) | 按字母顺序对 JSON 对象键进行排序 |
| complex_obj = json.dumps(4 + 5j, default=complex_encode) | Python 复杂对象编码到 JSON |
| JSONEncoder().encode(colour_dict) | 使用 JSONEncoder 类进行序列化 |
| json.loads(data_string) | 使用 json.loads() 函数将 JSON 字符串解码为 Python 字典 |
| json.loads(‘{“__complex__”: true, “real”: 4, “img”: 5}’, object_hook = is_complex) | 将复杂的 JSON 对象解码为 Python |
| JSONDecoder().decode(colour_string) | 使用反序列化将 JSON 解码为 Python |