Selenium 中的 TestNG @Test 优先级
TestNG 是一个测试框架,涵盖不同类型的测试设计,如单元测试、功能测试、端到端测试、UI 测试和集成测试。
您可以在您的TestNG代码中运行单个或多个测试用例。
如果在运行多个测试用例时未定义测试优先级,TestNG 会将所有 @Test 的优先级设置为零 (0)。
现在,在运行期间;较低优先级的将被优先调度。
没有优先级的 TestNG 代码演示
让我们来看一个需要按顺序执行才能通过所有测试用例的场景
场景:生成一段代码,要求您使用特定关键字(例如“Facebook”)执行 Google 搜索。现在,验证浏览器标题已更改为“Facebook – Google Search”。
注意:您编写的每个步骤都应在单独的方法中
方法 1:打开浏览器,例如 Firefox (openBrowser())
方法 2:启动 Google.com (launchGoogle())
方法 3:使用“Facebook”执行搜索 (performSearchAndClick1stLink())
方法 4:验证 Google 搜索页面标题 (FaceBookPageTitleVerification())
我们场景的代码:
import org.openqa.selenium.By;
import org.openqa.selenium.WebDriver;
import org.openqa.selenium.firefox.FirefoxDriver;
import org.testng.Assert;
import org.testng.annotations.Test;
public class Priority_In_testNG {
WebDriver driver;
// Method 1: Open Brower say Firefox
@Test
public void openBrowser() {
driver = new FirefoxDriver();
}
// Method 2: Launch Google.com
@Test
public void launchGoogle() {
driver.get("http://www.google.co.in");
}
// Method 3: Perform a search using "Facebook"
@Test
public void peformSeachAndClick1stLink() {
driver.findElement(By.xpath(".//*[@title='Search']")).sendKeys("Facebook");
}
// Method 4: Verify Google search page title.
@Test
public void FaceBookPageTitleVerification() throws Exception {
driver.findElement(By.xpath(".//*[@value='Search']")).click();
Thread.sleep(3000);
Assert.assertEquals(driver.getTitle().contains("Facebook - Google Search"), true);
}
}
代码解释
如上所述,我们创建了 4 个测试用例,用于在独立方法中执行每个操作。
- 第一个方法 (openBrowser) 用于初始化 Firefox 浏览器。
- 第二个方法 (launchGoogle) 用于在已初始化的浏览器中启动 Google.com。
- 第三个方法 (peformSeachAndClick1stLink) 用于在搜索框中执行搜索(使用 xpath (“.//*[@title=’Search’]”),搜索词为 Facebook),并且
- 第四个也是最后一个方法 (FaceBookPageTitleVerification) 用于点击 Google 的搜索图标并验证浏览器标题是否已更改为 Facebook – Google Search。
现在使用 TestNG 运行此代码,如视频中所示,您会发现所有测试用例都失败了。失败的原因是:由于依赖于上一个测试用例的通过,当前运行的测试用例才能通过。
在这种情况下,
- 执行的第一个方法是 openBrowser()。它通过了,因为它没有任何依赖性。
- 执行的第二个方法是 FaceBookPageTitleVerification(); 它失败了,因为我们试图点击搜索按钮并验证浏览器标题。
- 您可以看到,如果搜索活动没有进行,那么任何其他步骤都无法通过。因此,这就是我的测试用例失败的原因。
PASSED: openBrowser FAILED: FaceBookPageTitleVerification FAILED: launchGoogle FAILED: peformSeachAndClick1stLink
按字母顺序排列的没有优先级的 TestNG 代码演示
如果我们不指定任何优先级,TestNG 将根据 @Test 方法的名称的字母顺序执行它们,无论它们在代码中的实现位置如何。
package com.guru.testngannotations;
import org.testng.annotations.Test;
public class TestNG_Priority_Annotations {
@Test
public void c_method(){
System.out.println("I'm in method C");
}
@Test
public void b_method(){
System.out.println("I'm in method B");
}
@Test
public void a_method(){
System.out.println("I'm in method A");
}
@Test
public void e_method(){
System.out.println("I'm in method E");
}
@Test
public void d_method(){
System.out.println("I'm in method D");
}
}
输出
I'm in method A I'm in method B I'm in method C I'm in method D I'm in method E
尽管我们以随机方式(c、b、a、e、d)定义了这些方法,但 TestNG 仍根据方法的名称,按照字母顺序执行了这些方法,并且结果也反映了这一点。
如何在 TestNG 中设置优先级
正如您在前面的示例中看到的,为了通过此场景需要排序,因此我们将使用优先级参数修改前面的代码,以便每个测试都应根据分配给它们的优先级运行。
现在您可以看到,我们已为每个测试用例分配了优先级,这意味着优先级值较低的测试用例将首先执行。
TestNG 中的优先级操作
import org.openqa.selenium.By;
import org.openqa.selenium.WebDriver;
import org.openqa.selenium.firefox.FirefoxDriver;
import org.testng.Assert;
import org.testng.annotations.Test;
public class Priority_In_testNG {
WebDriver driver;
// Method 1: Open Browser say Firefox
@Test (priority=1)
public void openBrowser() {
driver = new FirefoxDriver();
}
// Method 2: Launch Google.com
@Test (priority=2)
public void launchGoogle() {
driver.get("http://www.google.co.in");
}
// Method 3: Perform a search using "Facebook"
@Test (priority=3)
public void peformSeachAndClick1stLink() {
driver.findElement(By.xpath(".//*[@title='Search']")).sendKeys("Facebook");
}
// Method 4: Verify Google search page title.
@Test (priority=4)
public void FaceBookPageTitleVerification() throws Exception {
driver.findElement(By.xpath(".//*[@value='Search']")).click();
Thread.sleep(3000);
Assert.assertEquals(driver.getTitle().contains("Facebook - Google Search"), true);
}
}
代码解释
为每个测试用例分配优先级后,使用 TestNG 运行上述代码,如以下视频 2 中所示。
这里,您可以看到测试用例已设置了优先级。优先级较低的测试用例首先执行,即现在测试用例中的执行是按优先级顺序进行的。因此,所有测试用例现在都通过了。
注意 Eclipse 的控制台
输出:
PASSED: openBrowser PASSED: launchGoogle PASSED: peformSearchAndClick1stLink PASSED: FaceBookPageTitleVerification
数字 0 具有最高优先级(它将首先执行),优先级根据给定的数字依次递减,即 0 的优先级高于 1。1 的优先级高于 2,依此类推。
package com.guru.testngannotations;
import org.testng.annotations.Test;
public class TestNG_Priority_Annotations {
@Test(priority=6)
public void c_method(){
System.out.println("I'm in method C");
}
@Test(priority=9)
public void b_method(){
System.out.println("I'm in method B");
}
@Test(priority=1)
public void a_method(){
System.out.println("I'm in method A");
}
@Test(priority=0)
public void e_method(){
System.out.println("I'm in method E");
}
@Test(priority=3)
public void d_method(){
System.out.println("I'm in method D");
}
}
输出
I'm in method E I'm in method A I'm in method D I'm in method C I'm in method B
这里我们提供的优先级为 0,1,3,6,9。因此,优先级为 0 的方法首先执行,然后是优先级为 1 的方法,依此类推。由于我们提供了优先级,因此这里不考虑字母顺序方法名。
相同优先级的方法
方法可能包含相同的优先级。在这些情况下,TestNG 会考虑具有相同优先级的方法名称的字母顺序。
package com.guru.testngannotations;
import org.testng.annotations.Test;
public class TestNG_Priority_Annotations {
@Test(priority=6)
public void c_method(){
System.out.println("I'm in method C");
}
@Test(priority=9)
public void b_method(){
System.out.println("I'm in method B");
}
@Test(priority=6)
public void a_method(){
System.out.println("I'm in method A");
}
@Test(priority=0)
public void e_method(){
System.out.println("I'm in method E");
}
@Test(priority=3)
public void d_method(){
System.out.println("I'm in method D");
}
}
输出
I'm in method E I'm in method D I'm in method A I'm in method C I'm in method B
这里的“e”和“d”是根据它们的优先级值执行的。但是方法“a”和“c”具有相同的优先级值 (6)。因此,TestNG 会考虑“a”和“c”的字母顺序并相应地执行它们。
结合优先(具有相同优先级)和非优先方法
在这种情况下,我们将在一个 testng 类中涵盖两种情况。
- 具有相同优先级值的方法。
- 多个未设置优先级的方法。
package com.guru.testngannotations;
import org.testng.annotations.Test;
public class TestNG_Priority_Annotations {
@Test()
public void c_method(){
System.out.println("I'm in method C");
}
@Test()
public void b_method(){
System.out.println("I'm in method B");
}
@Test(priority=6)
public void a_method(){
System.out.println("I'm in method A");
}
@Test(priority=0)
public void e_method(){
System.out.println("I'm in method E");
}
@Test(priority=6)
public void d_method(){
System.out.println("I'm in method D");
}
}
输出
I'm in method B I'm in method C I'm in method E I'm in method A I'm in method D
PASSED: b_method PASSED: c_method PASSED: e_method PASSED: a_method PASSED: d_method
解释
第一优先级:未设置优先级的方法:“c”和“b”:根据字母顺序,“b”先执行,然后是“c”。
第二优先级:已设置优先级的方法:“a”、“e”和“d”:“e”首先执行,因为它具有最高优先级 (0)。由于“a”和“d”方法的优先级相同,TestNG 考虑了它们方法名称的字母顺序。因此,在它们之间,“a”首先执行,然后是“d”。
TestNG 中的大小写敏感性
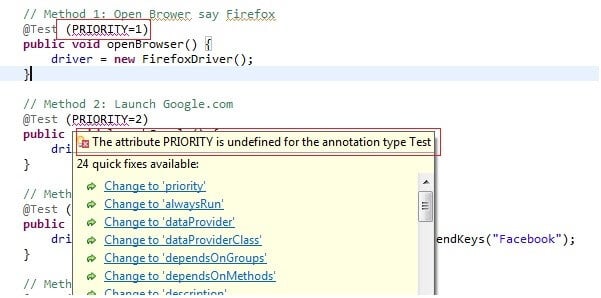
仅供参考,TestNG 中定义优先级的标准语法是@Test (priority=4),假设您使用其他语法定义它,例如@Test (PRIORITY=1),那么您的 IDE 将显示编译错误。请参考下图
结论
正如您所看到的,如果需要以特定顺序运行一组测试用例,那么使用 TestNG 作为运行工具,使用优先级可以轻松实现。
本教程的完成得益于 Ramandeep Singh 和 Rama Krishna Gadde 的贡献