Python 列表 Append() 示例
Python 中的 Append 方法是什么?
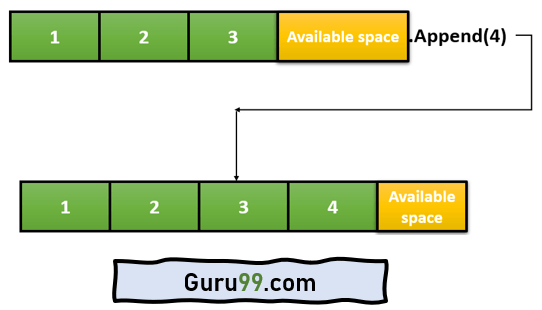
Python 中的 append 函数有助于将新元素插入到基础列表中。元素会被追加到现有列表的右侧。append 方法接受一个参数,并将列表的大小增加 1。
下图说明了 Python 的 append 函数
语法
List.append(object)
注意:此处,对象可以是整数、字符串或浮点数。append 函数不返回任何值或列表。它会修改并增长基础列表。
如何使用 Append 函数创建 Python 列表?
Python 列表可以通过两种方法创建和填充。
- 第一种方法使用列表推导式。
- 第二种方法利用 Append 函数和“for 循环”。在这种方法中,您可以创建一个使用 for 循环和 append 的用户定义函数。
请看下面使用第二种方法的示例: –
import math
def calc_sqr_root(b_list):
bop=[]
for number in b_list:
bop.append(math.sqrt(number))
return bop
base_list=(4,9,100,25,36,49,81)
print("the Squared number list is as follows",base_list)
calc_sqr_root(base_list)
print("the numbers with square root in list is as follows",calc_sqr_root(base_list))
输出
the Squared number list is as follows (4, 9, 100, 25, 36, 49, 81) the numbers with square root in the list is as follows [2.0, 3.0, 10.0, 5.0, 6.0, 7.0, 9.0]
代码解释
- 使用方括号定义一个空列表。
- for 循环和 append 函数一起在用户定义的函数中使用。
- 它从头开始填充一个空列表。
- 它通过使用 for 循环插入元素来逐个插入单个元素。
- 追加的列表用于为用户定义的函数返回值。
下面是使用第一种方法的示例
示例
Python 代码
import math
def calc_sqr_root(b_list):
return [math.sqrt(number) for number in b_list]
base_list=(4,9,100,25,36,49,81)
print("the Squared number list is as follows",base_list)
calc_sqr_root(base_list)
print("the numbers with square root in list is as follows",calc_sqr_root(base_list))
输出
the Squared number list is as follows (4, 9, 100, 25, 36, 49, 81) the numbers with a square root in the list are as follows [2.0, 3.0, 10.0, 5.0, 6.0, 7.0, 9.0]
代码解释
- 您可以使用列表推导式作为 Python 中 append 函数的替代品,从头开始填充列表。
- 它有助于从一开始就填充列表。
- 自定义列表下的列表推导式有助于填充原始列表中的元素。
- 与 for 循环和 append 函数的组合相比,它有助于优化数据处理。
Append 方法如何工作?
Append 函数以以下方式提供帮助: –
- Python 中的 Append 函数将对象添加到基础列表中。
- 它将对象作为参数,并将其放置在下一个空位。
- 列表项是有序的,可以使用索引访问。
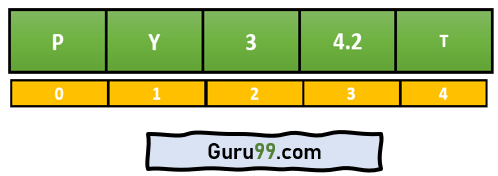
下面是一张显示元素索引的图片
让我们来看下面的例子,它将元素添加到基础列表中。
Python 示例
baselist = ['P','Y','3','4.2','T']
print("The original list", baselist)
print("At index 0:", baselist[0])
print("At index 3:",baselist[3])
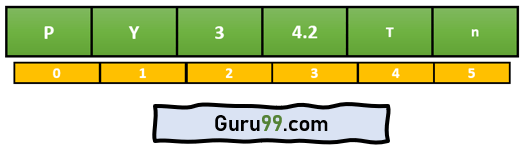
baselist.append('n')
print("The appended list", baselist)
print("At index 5 post append:",baselist[5])
输出
The original list ['P', 'Y', '3', '4.2', 'T'] At index 0: P At index 3: 4.2 The appended list ['P', 'Y', '3', '4.2', 'T', 'n'] At index 5 post append: n
代码解释
- Append 函数将对象的对象数据类型添加到列表中可用的保留空间。
- Python 列表是可迭代序列,可以包含不同的数据类型和对象。
append 函数将新元素添加到索引 5,如下所示: –
如何在不使用 Append 的情况下将元素插入列表?
如果未使用 append 函数,程序员可以通过执行两步过程将元素添加到列表中。
使用 Len 函数,您可以找出列表中最后一个元素 的长度。将确定的空位分配给新对象。下面的示例说明了该概念: –
示例
base_list=[2,4,6]
print("The list before append",base_list)
base_list[len(base_list):]=[10]
print("The list after append",base_list)
输出
The list before append [2, 4, 6] The list after append [2, 4, 6, 10]
如何使用 Append 函数定义堆栈?
堆栈具有以下适用属性: –
- 堆栈可以定义为一种数据结构,它将项目堆叠在一起。
- 项目可以按后进先出(LIFO)原则插入或删除。
- 通常,堆栈将项目推入堆栈的末尾或顶部,而弹出操作则从堆栈中移除项目。
- append 函数充当堆栈的 push 操作,而列表默认具有用于移除项目的 pop 函数。
- 当未向 pop 函数指定任何参数时,pop 方法默认会返回并移除列表中的最后一个项目。
- 当列表变空时,它会引发索引错误。
- 如果为该函数提供了整数参数,则它会返回列表的索引。
- 它会移除列表中位于该索引处的项目。
让我们看一个程序,其中 append 和 pop 函数作为定义堆栈的 push 和 pop 操作
示例
Python 代码
#initialize the stack
GGGstack = []
print("Adding item to the list",GGGstack.append(100))
print("Adding item to the list",GGGstack.append(2333))
print("Adding item to the list",GGGstack.append(50000))
print("the base list after adding elements,",GGGstack)
print("base list after calling pop",GGGstack.pop())
print("base list after calling pop",GGGstack.pop())
print("base list after calling pop",GGGstack.pop())
print("base list after calling pop",GGGstack.pop())
输出
Adding item to the list None Adding item to the list None Adding item to the list None the base list after adding elements, Stack([100, 2333, 50000]) base list after calling pop 50000 base list after calling pop 2333 base list after calling pop 100 Empty stack base list after calling pop None
代码解释
- 定义了一个名为 GGGStack 的堆栈
- 使用 append 方法添加项目
- 每个项目都会从原始列表中逐一弹出。
- 当列表为空时,会引发索引错误。
Python 中的 Extend 方法是什么?
Extend 函数允许向可迭代列表添加新元素。可迭代列表的示例包括字典、元组和字符串。这些属性可帮助您修改可迭代列表中的元素。
注意:此函数在执行后不返回任何值。
以下是 extend 函数的语法: –
语法
List.extend(iterable list)
Python 中 Extend 和 Append 的区别
- Python 中的 append 函数仅向原始列表添加一个元素,而 extend 函数允许添加多个项目。
- append 列表仅接受一个参数,而 extend 函数接受可迭代列表,如元组和字典。
结论
- append 函数有助于在原始列表的末尾添加项目。
- 可以使用 for 循环和 append 函数将多个项目添加到列表中。